
Benefits and Side Effects of Sweet Potatoes: A Comprehensive Guide

Sweet potatoes are a highly nutritious and popular food enjoyed worldwide. They are not only delicious and versatile but also offer numerous health benefits. However, consuming them incorrectly or excessively may lead to unwanted side effects. Let’s explore the benefits and potential risks of sweet potatoes and how to consume them properly for optimal health.
1. Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes
1.1. A Nutritional Powerhouse
Sweet potatoes are packed with essential nutrients, including:
- Vitamins and minerals: Rich in vitamin A (as beta-carotene), vitamin C, B6, potassium, and manganese.
- Dietary fiber: Supports digestion, helps control blood sugar, and improves heart health.
- Antioxidants: Protect the body from oxidative stress, slow aging, and prevent chronic diseases.
1.2. Supports Digestion and Prevents Constipation
- The high fiber content in sweet potatoes promotes bowel movements and prevents constipation.
- They also contain prebiotics that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, improving digestive health.
1.3. Helps Regulate Blood Sugar Levels
- Sweet potatoes have a moderate glycemic index (GI), meaning they do not cause rapid spikes in blood sugar.
- Some studies suggest that sweet potatoes can enhance insulin sensitivity, benefiting people with diabetes.
1.4. Improves Vision Health
- Rich in vitamin A (beta-carotene), sweet potatoes help maintain eye health, protect the retina, and reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
1.5. Reduces Inflammation and Strengthens Immunity
- Sweet potatoes contain anti-inflammatory compounds that may help reduce chronic inflammation, benefiting conditions like arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- High levels of vitamin C, beta-carotene, and manganese boost the immune system and reduce susceptibility to infections.
1.6. Supports Heart Health
- Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of potassium, which helps regulate blood pressure and reduce the risk of stroke and heart disease.
- The fiber and antioxidants in sweet potatoes may help lower bad cholesterol (LDL), further protecting cardiovascular health.
1.7. Aids in Weight Management
- Sweet potatoes are nutrient-dense, low in calories, and high in fiber, making them a great food for weight management.
- Their complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, preventing excessive calorie intake.
1.8. Promotes Healthy Skin and Anti-Aging
- The high levels of vitamin C and E in sweet potatoes support collagen production, keeping skin firm and reducing wrinkles.
- Antioxidants protect the skin from UV damage and environmental stressors.
2. Potential Side Effects of Overconsumption
Despite their numerous health benefits, eating too many sweet potatoes or consuming them improperly can lead to unwanted effects.
2.1. May Increase the Risk of Kidney Stones
- Sweet potatoes are high in oxalates, which can contribute to kidney stone formation, especially in individuals prone to kidney issues.
- They are also rich in potassium, so people with kidney disease should limit their intake to prevent hyperkalemia(excess potassium in the blood).
2.2. May Cause Digestive Discomfort
- Sweet potatoes contain mannitol, a type of carbohydrate that may cause bloating, stomach pain, or diarrhea in individuals with sensitive digestive systems.
- If you have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), consume sweet potatoes in moderation.
2.3. May Raise Blood Sugar Levels if Overeaten
- While sweet potatoes have a moderate glycemic index, eating too much (especially roasted or fried sweet potatoes) can increase blood sugar levels, which may be problematic for diabetics.
2.4. Risk of Vitamin A Toxicity
- Sweet potatoes are extremely high in vitamin A, and excessive consumption may lead to vitamin A toxicity, causing:
- Headaches, dizziness, nausea.
- Dry, flaky skin, hair loss, and cracked lips.
- Long-term excessive intake can cause liver damage.
📌 Recommended daily vitamin A intake:
- Men: 900 mcg.
- Women: 700 mcg.
- If you are already getting vitamin A from other sources, be mindful of your sweet potato consumption.
2.5. Excess Potassium May Affect Heart Health
- While potassium is essential for heart health, excessive intake may cause hyperkalemia, leading to:
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Increased risk of heart complications.
3. How to Eat Sweet Potatoes Correctly for Maximum Benefits
3.1. How Much Sweet Potato Should You Eat Daily?
- For healthy individuals: 100–150g per day.
- For diabetics or overweight individuals: 50–100g per day, preferably boiled.
- For individuals with kidney or heart conditions: Consult a doctor before consuming sweet potatoes regularly.
3.2. Best Ways to Eat Sweet Potatoes
✅ Boiling or steaming is the healthiest way to consume sweet potatoes, as it preserves nutrients and prevents a high glycemic index.
✅ Pair sweet potatoes with protein-rich foods (meat, eggs, beans, dairy) or leafy greens for a balanced diet.
✅ Avoid eating sweet potatoes late at night to prevent bloating and indigestion. The best time to eat them is in the morning or at lunchtime.
✅ Store sweet potatoes in a cool, dry place and avoid eating sprouted sweet potatoes, as they may contain harmful compounds.
Conclusion
Sweet potatoes are an excellent addition to a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. However, overconsumption or improper preparation may lead to health issues. To maximize their benefits, consume them in appropriate portions, cook them properly, and balance your overall diet.
👉 Make sweet potatoes a part of your nutritious diet and enjoy their many health benefits! 🚀
News in the same category


Natural BOMB 🍊🍯 for Cleansing the Liver and Blood Vessels: 3 Old Forgotten Recipes!(With Ginger, Beet, and Carrot)

Transform Your Health with a Secret Mix of Parsley and Apple! 🍏🌿

Supporting Joint Health Naturally

Soothe Knee and Joint Discomfort with Nature’s Secret Tea Blend

Making the Most of Avocados with Dark Spots
Discover the Power of Garlic Against Infections

Discover the Hidden Value of Lemon Seeds 🍋✨

If You Start Preparing Nopal with Beetroot, You’ll Thank Me Forever

Discover the Magic of Cabbage Leaves for Joint Comfort

The Avocado Seed: What It’s Good For and Its Potential Health Benefits 🥑

The Leaves That Heal: A Natural Remedy for Diabetes, Poor Circulation, High Blood Pressure, and Even Cancer – No Pills Needed

Natural Remedy to Eliminate Type 2 Diabetes, Cholesterol, Obesity, Poor Circulation, Arthritis, Fatty Liver, and More

Dr. Frank Suárez’s Natural Remedy to Prevent Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, Poor Circulation, and Even Cancer
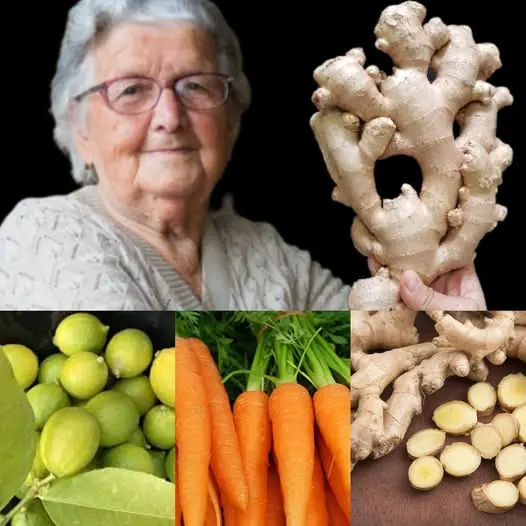

Cleanse Your Intestines and Liver Naturally with Ginger, Lemon, and Carrot
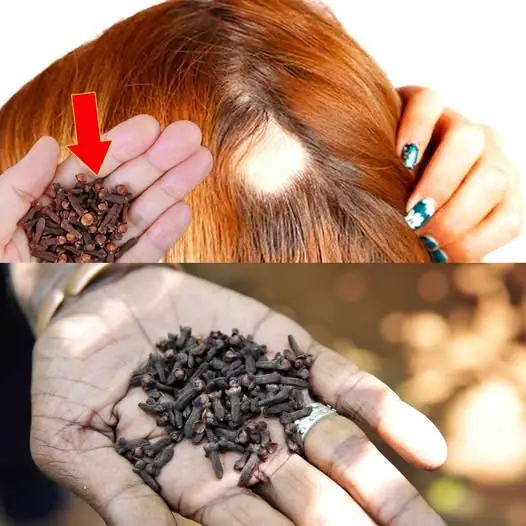

Transform Your Hair with the Power of Cloves
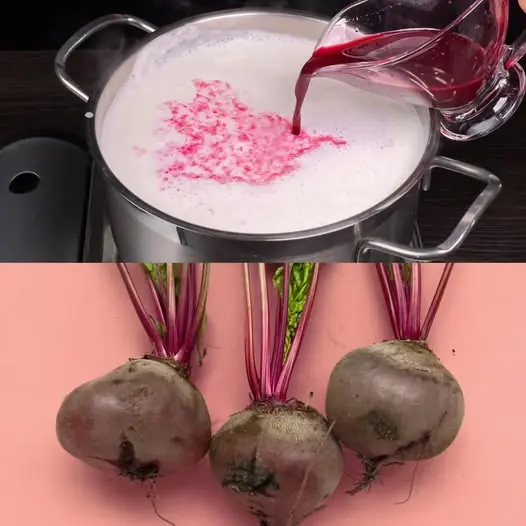

Uncover the Magic of Beet and Milk Soup: A Simple 3-Ingredient Recipe
Enhance Your Beauty Overnight with Castor Oil
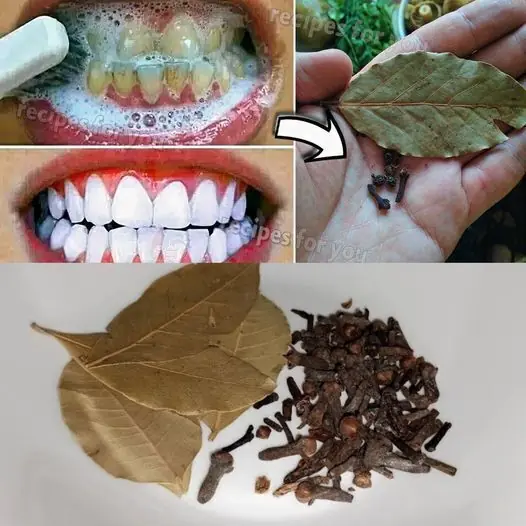

Achieving a Brighter Smile Naturally with Cloves and Bay Leaves

🌿 THE NATURAL REMEDY DR. SUÁREZ RECOMMENDED
News Post

Warning from K Hospital: Daily Consumption of Certain Meats May Increase Cancer Risk – Don’t Take It Lightly!

How One Cancer Survivor Triggered Interest in Repurposed Anti-Parasitic Drugs

Glee star Cory Monteith's parents tragically die weeks apart following his death 12 years ago

8 Uses for Epsom Salt Few People Know About

Natural BOMB 🍊🍯 for Cleansing the Liver and Blood Vessels: 3 Old Forgotten Recipes!(With Ginger, Beet, and Carrot)

Transform Your Health with a Secret Mix of Parsley and Apple! 🍏🌿

Supporting Joint Health Naturally

Soothe Knee and Joint Discomfort with Nature’s Secret Tea Blend

Making the Most of Avocados with Dark Spots

Discover the Power of Garlic Against Infections

Discover the Hidden Value of Lemon Seeds 🍋✨

If You Start Preparing Nopal with Beetroot, You’ll Thank Me Forever

Discover the Magic of Cabbage Leaves for Joint Comfort

The Avocado Seed: What It’s Good For and Its Potential Health Benefits 🥑

The Leaves That Heal: A Natural Remedy for Diabetes, Poor Circulation, High Blood Pressure, and Even Cancer – No Pills Needed
5 Essential Leaves to Naturally Improve Your Eye Health
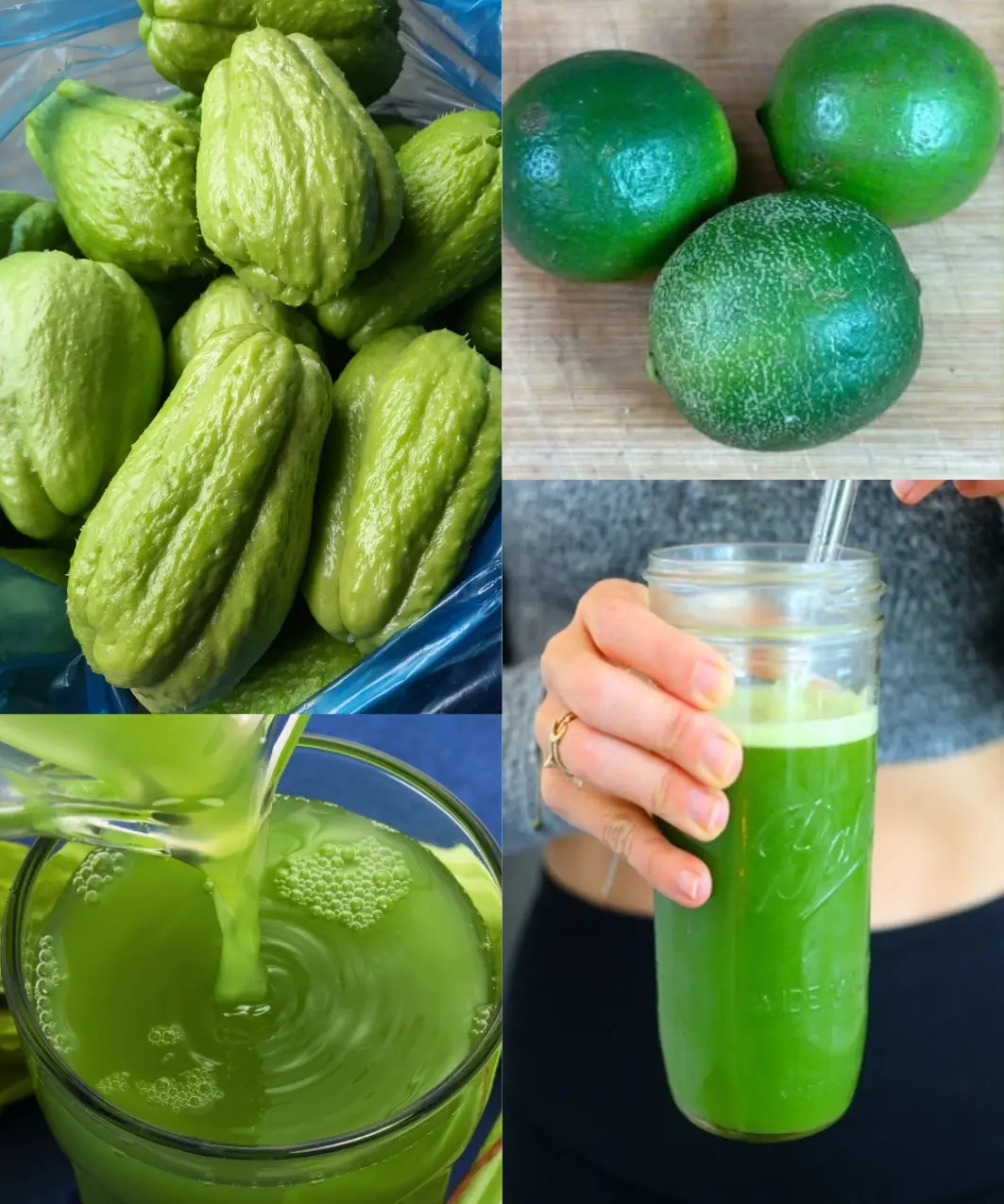

16 Benefits of Chayote Juice: Say Goodbye to Pills and Hello to Natural Healing
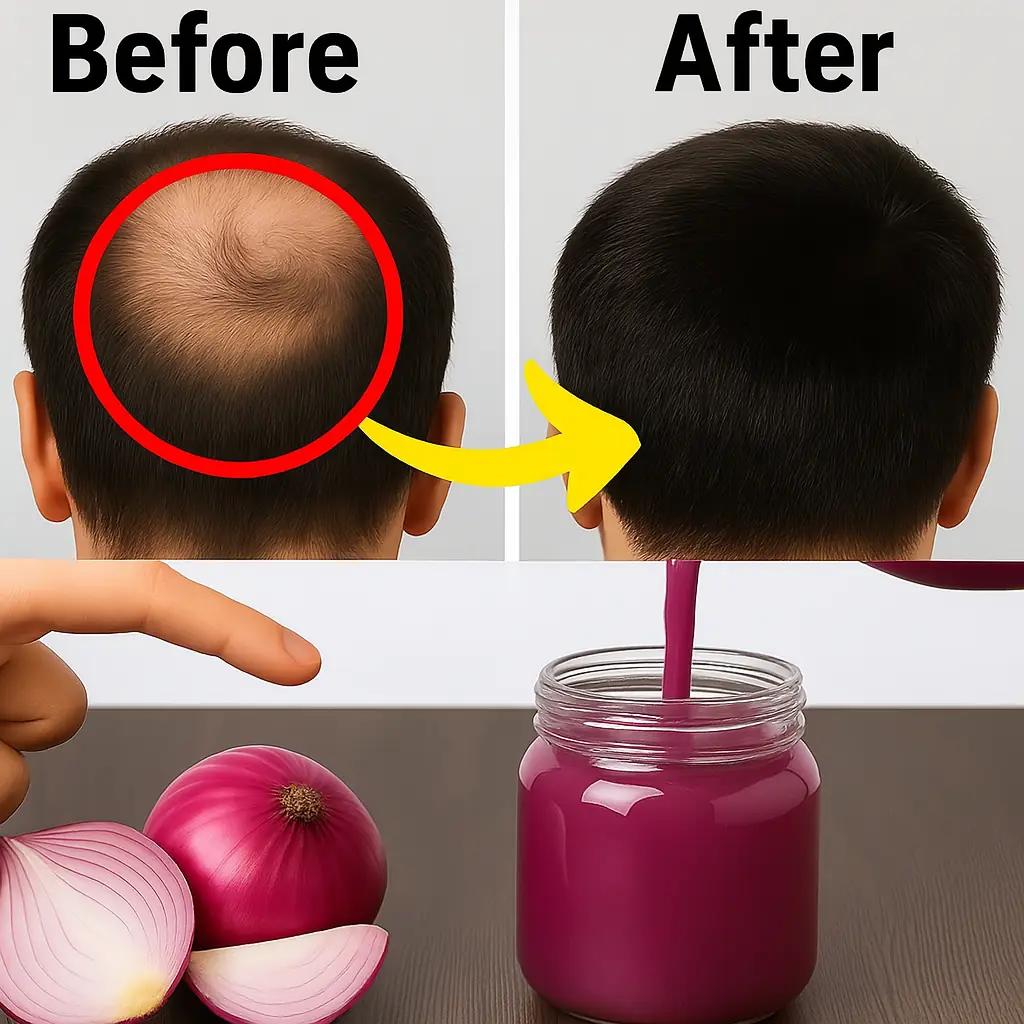

Red Onion for Hair Growth: A Natural Remedy for Thinning Hair
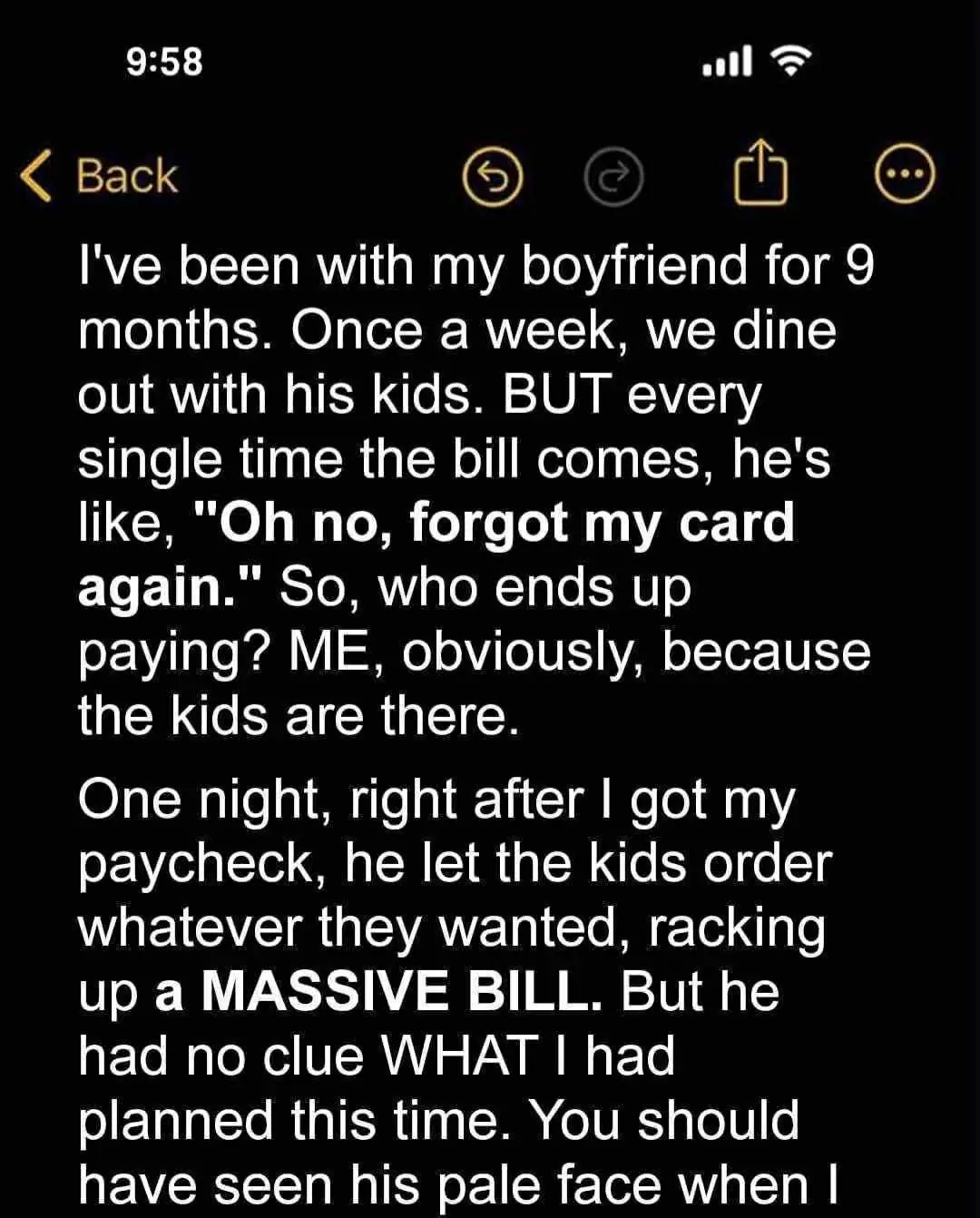
My boyfriend always ‘forgets’ his credit card when we eat out, so I have to foot the bill
