China’s Dark Factories: Ushering in a Fully Automated Manufacturing Era
March 19, 2025 — China has officially stepped into the future of industrial production with the rise of so-called dark factories—fully automated manufacturing facilities that operate without human workers, and often without the need for lighting at all. These next-generation plants rely on advanced robotics, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things (IoT) networks to function around the clock, cutting costs while boosting output and consistency.
The shift marks one of the most significant transformations in modern industrial history. With machines now capable of handling every stage of production, global labor markets, supply chains, and energy use are all being reshaped at unprecedented speed.
What Exactly Is a Dark Factory?
A dark factory is a production facility where human involvement is almost entirely eliminated. Robots and AI systems manage tasks such as assembly, packaging, quality control, and logistics. Because machines do not require light, heating, or breaks, these factories often run literally “in the dark.”
Such operations depend on interconnected AI and IoT systems that coordinate machines in real time, ensuring precision, efficiency, and continuous production. From raw material handling to final product assembly, the process is fully automated.
Why Companies Are Embracing Dark Factories
-
24/7 Efficiency: Machines operate continuously, eliminating downtime.
-
Reduced Costs: Lower labor expenses and optimized energy consumption.
-
Consistent Quality: AI systems maintain strict quality standards and detect defects instantly.
-
Sustainability: Automation minimizes waste and reduces carbon footprints.
Key Features of Fully Automated Facilities
-
End-to-End Automation
Robots and AI manage entire production lines, from warehouse logistics to final packaging. -
Intelligent Machine Networks
IoT-linked systems communicate seamlessly, enabling predictive maintenance and self-adjustments. -
AI-Powered Quality Control
Machine learning algorithms analyze products at microscopic levels, identifying even the smallest inconsistencies. -
Ultra-Clean Environments
Automated purification systems maintain sterile conditions ideal for pharmaceuticals, electronics, and aerospace. -
Scalable, High-Speed Production
AI systems can instantly adapt production levels to meet fluctuating demand. -
Energy-Efficient Operations
Smart energy management reduces waste and environmental impact.
China Leads the Automation Push
Beijing has made automation a national priority. Through initiatives like “Made in China 2025,” the government is heavily funding AI-driven manufacturing to maintain China’s dominance as the world’s leading producer.
Global corporations are following suit. Automotive, semiconductor, and pharmaceutical giants are investing billions in similar facilities, spreading the dark factory model across Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia.
The Benefits and the Costs
Dark factories promise:
-
Higher productivity through uninterrupted 24/7 operation.
-
Enhanced product quality via self-improving AI inspection.
-
Greener manufacturing with optimized energy use.
But there are also challenges:
-
Job displacement, as millions of workers in traditional factories risk redundancy.
-
Cybersecurity risks, since fully connected AI systems are vulnerable to hacking.
-
Ethical concerns, as AI makes decisions once controlled by humans, raising questions of accountability and transparency.
How Dark Factories Could Reshape Global Trade
The rise of automation could alter international trade patterns. With efficiency gains, some companies may bring manufacturing back to developed countries, reducing dependence on offshore labor. Nations leading in AI manufacturing are poised to dominate global supply chains, while traditional low-cost labor markets may face steep economic adjustments.
The Future of Manufacturing
Dark factories are no longer futuristic concepts—they are operational realities. By combining robotics, AI, and IoT, these facilities represent a dramatic leap forward in industrial capability.
While they promise efficiency, scalability, and sustainability, they also force society to confront difficult questions about the future of work, ethics in AI, and economic balance.
As automation accelerates, one thing is clear: fully autonomous factories will not just transform manufacturing—they will redefine the global economy itself.
News in the same category


How 15,000 Bikers Rallied in Germany to Fulfill a Dying Boy’s Dream

Nick Vujicic: Living Without Limbs, Inspiring Millions Worldwide

The Giant Pink Rabbit of Italy: From Knitted Monument to Decaying Legacy
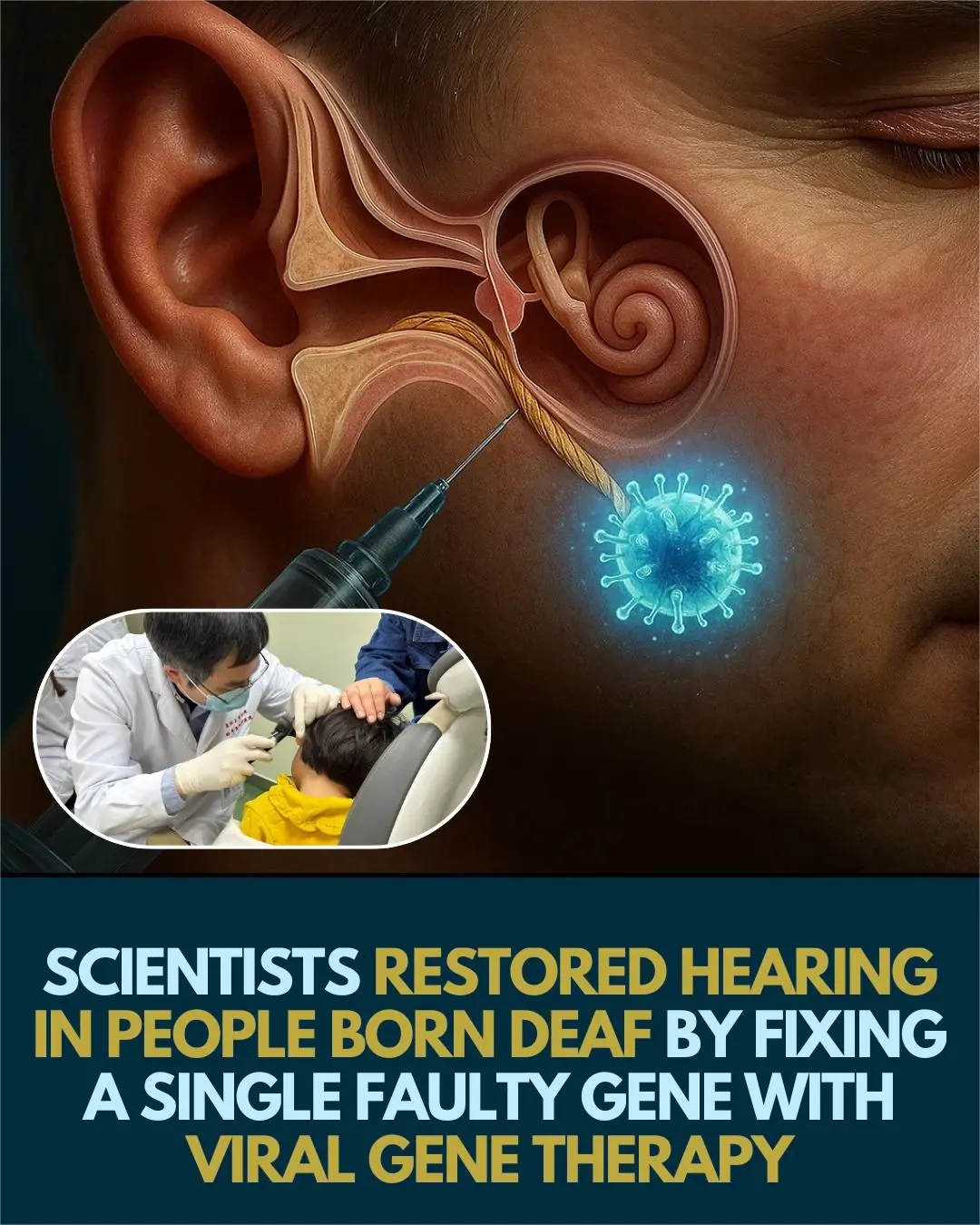
Gene Therapy Breakthrough: Restoring Hearing in Deaf Individuals via Single-Gene Repair

Giant Manta Ray Approaches Divers for Help in Removing Fishing Hooks

Brooklyn Homeowner Loses $800,000 House Over a $5,000 Water Bill

La Niña Returns: Colder Winter Expected Worldwide

2 injured in crash involving 3 commercial vehicles in Wood County

From lab coat to red carpet: Bill Nye receives star on Hollywood Walk of Fame

Emerging Evidence Raises Questions About Tattoo Ink and Cancer Risk

From Selling Pens on the Streets to Inspiring the World: A Father’s Story of Love and Resilience

Winchcombe Meteorite: A Pristine Messenger from Space That Carries the Building Blocks of Life

RFK Jr. Calls for Restrictions on 5G Towers, Citing Health and Safety Concerns

Young Hero: Bridger Walker, the Boy Who Saved His Sister from a Dog Attack

Doppelgänger Surprise: Two Strangers Look Exactly Alike on Flight
Researchers Edge Closer to a Universal Cancer Vaccine as Human Trials Loom

Chinese Family Devours 5.5kg of Durian Outside Thailand Airport After Flight Ban
News Post

From Foster Care to Fatherhood: One Man’s Mission to Keep Five Siblings Together
15 Deadly Kidney Signs You Must Catch Early
13 Early Signs of Kidney Failure (You Ignore Daily) | Symptoms of Kidney Failure

Japan’s Innovative Parenting Lesson Lets Teens Experience Pregnancy and Infant Care

A New Bird Just Appeared in Texas—and That’s Not a Good Thing
Unlock Garlic’s Hidden Powers: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Health with Nature’s Superfood

Can Okra Water Unlock a Hidden Health Revolution for You? Discover the Secret Elixir
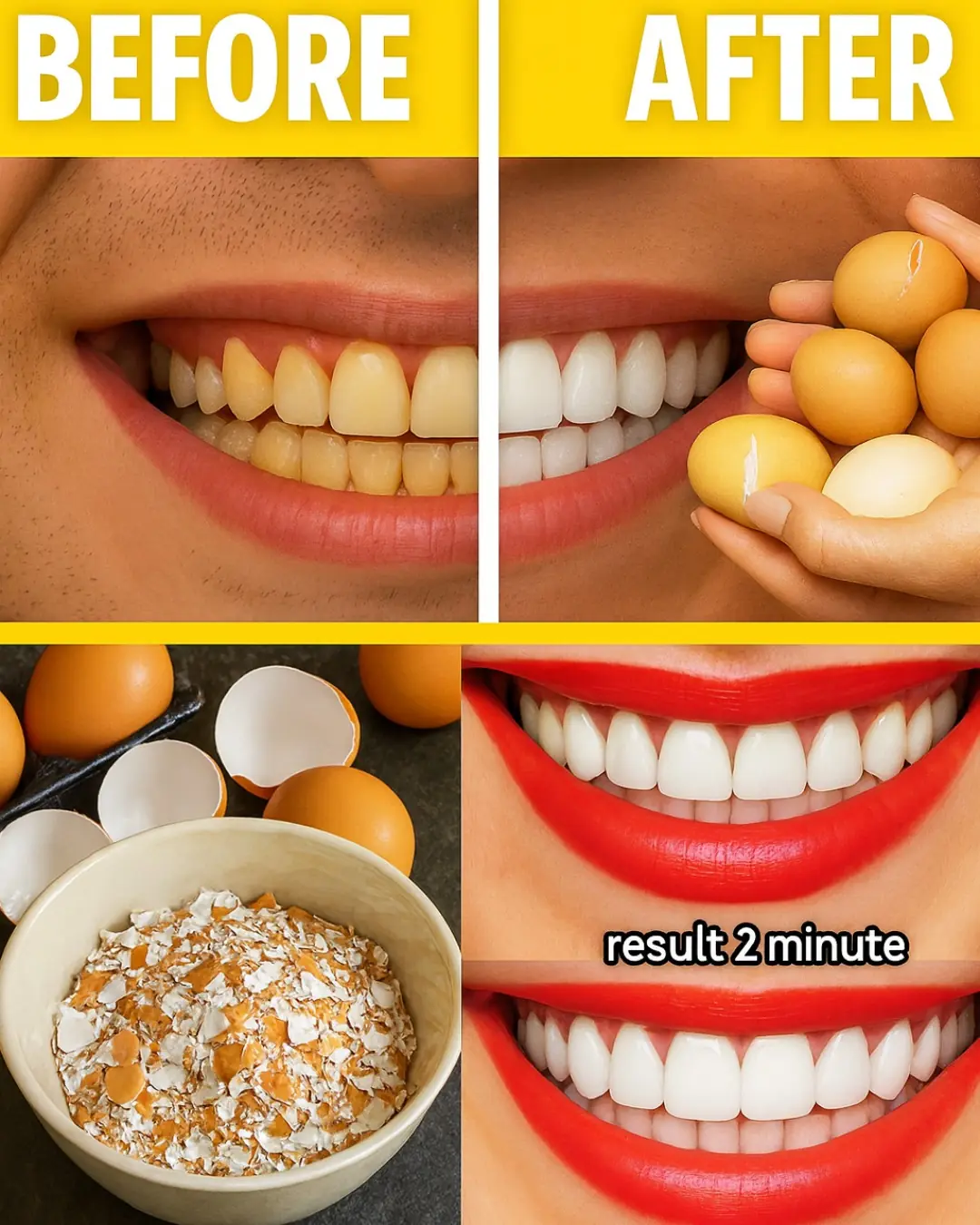

Can Kitchen Staples Unveil a Dazzling Smile in 5 Minutes?

How 15,000 Bikers Rallied in Germany to Fulfill a Dying Boy’s Dream

Nick Vujicic: Living Without Limbs, Inspiring Millions Worldwide
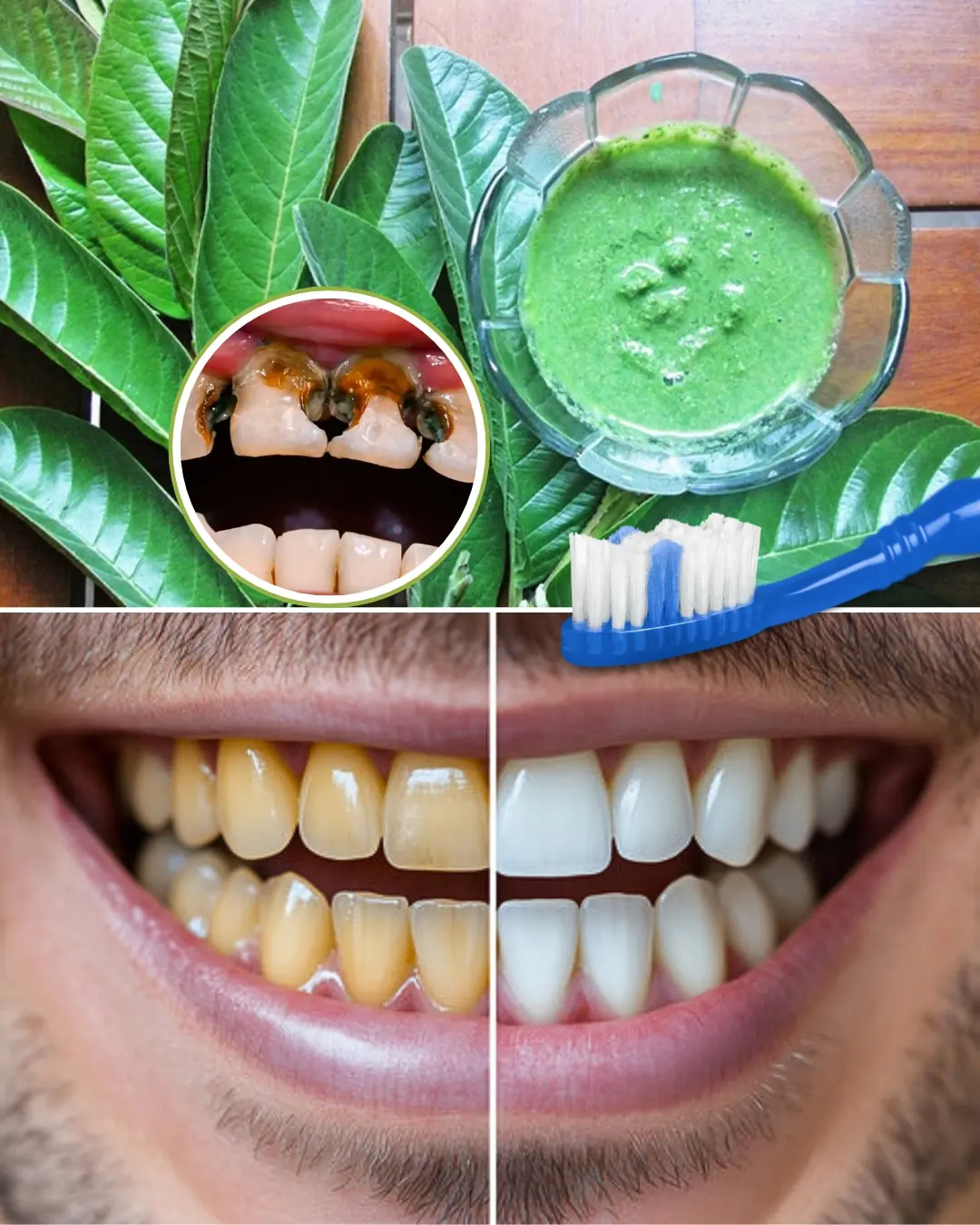

Grandma’s Shocking Secret to a Hollywood Smile: Guava Leaves Unveiled!
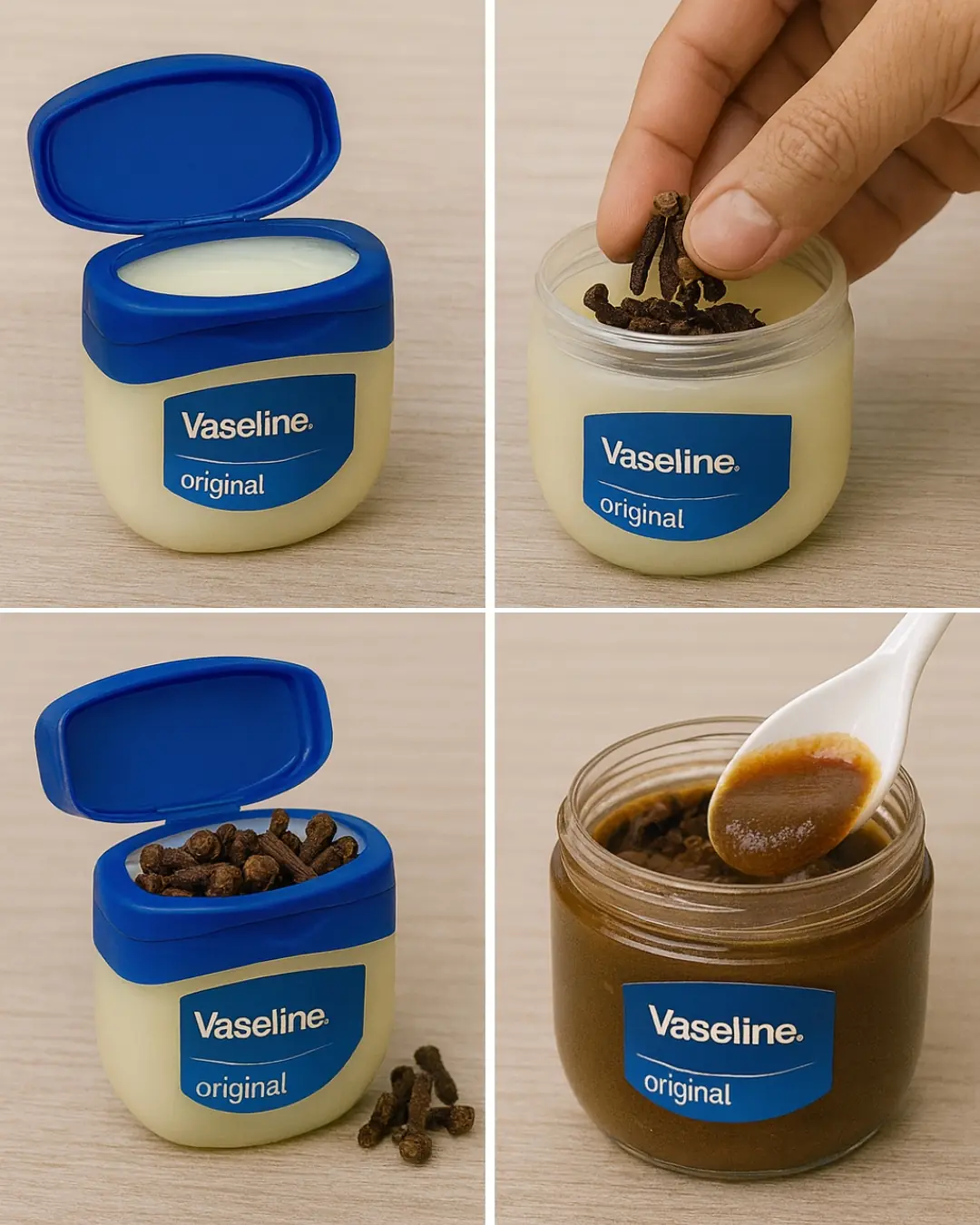

Mix Cloves with Vaseline: A Secret Nobody Will Ever Tell You (Thank Me Later)

The Giant Pink Rabbit of Italy: From Knitted Monument to Decaying Legacy

Gene Therapy Breakthrough: Restoring Hearing in Deaf Individuals via Single-Gene Repair

Giant Manta Ray Approaches Divers for Help in Removing Fishing Hooks

See the Difference: A Delicious Drink to Support Eye Health Naturally
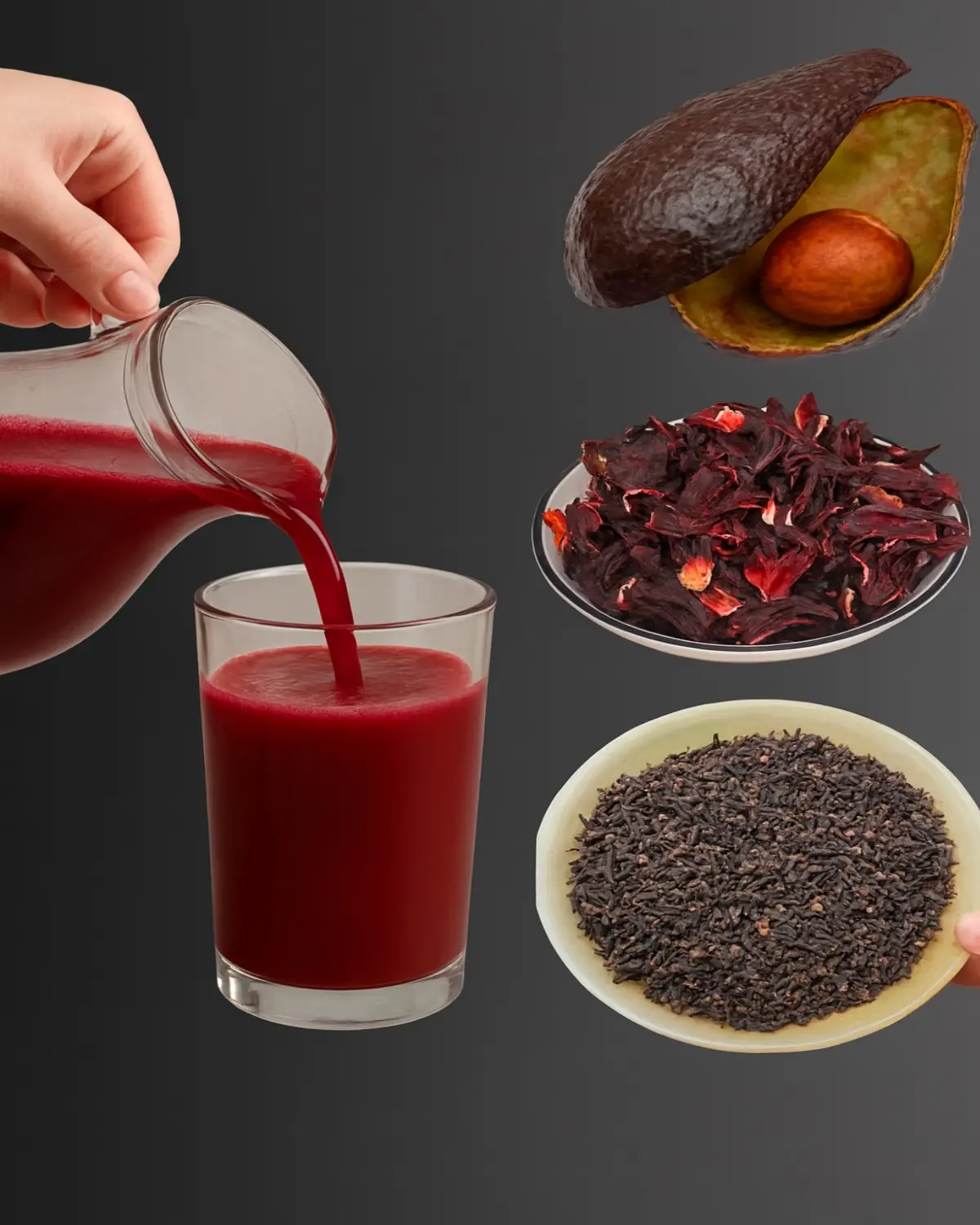

Avocado, Hibiscus & Clove Smoothie: A Vibrant Blend for Energy, Digestion & Glow

Take Honey and Cloves After 50: Fix 13 Common Health Issues in One Week!

A 4-Year-Old Girl Nearly Lost Her Life Due to Diabetes, Parents Cried: “We Spoiled Her Too Much!”