
Garden 2025-03-03 02:44:28
How to Grow Lots of Ginger in Containers
Growing ginger in containers is an easy and rewarding process that yields a plentiful harvest, even in small spaces.
News in the same category

Garden 27/08/2025 09:24
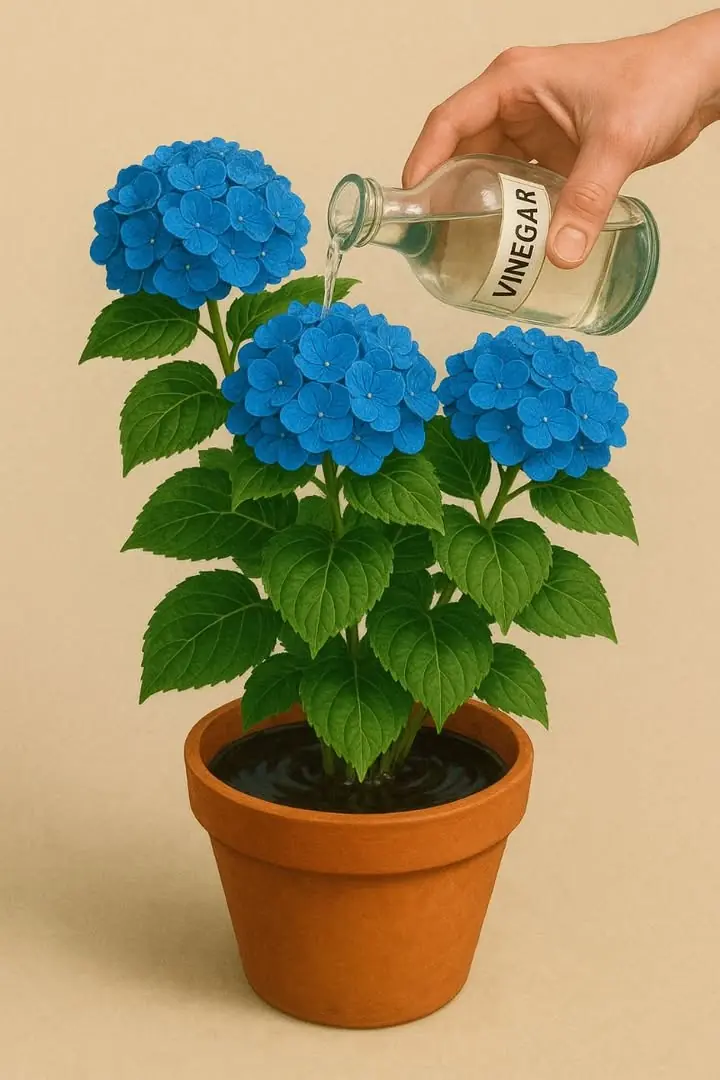

Vinegar makes hydrangeas bloom and bluer? 13 best garden hacks most don’t know
Garden 27/08/2025 09:22

THE MONEY PLANT
Garden 13/06/2025 23:19

7 Reasons Why You Shouldn’t Kill Purslane in Your Garden
Garden 08/03/2025 02:32

15 Most Useful Citrus Peel Uses in The Garden
Garden 08/03/2025 02:29
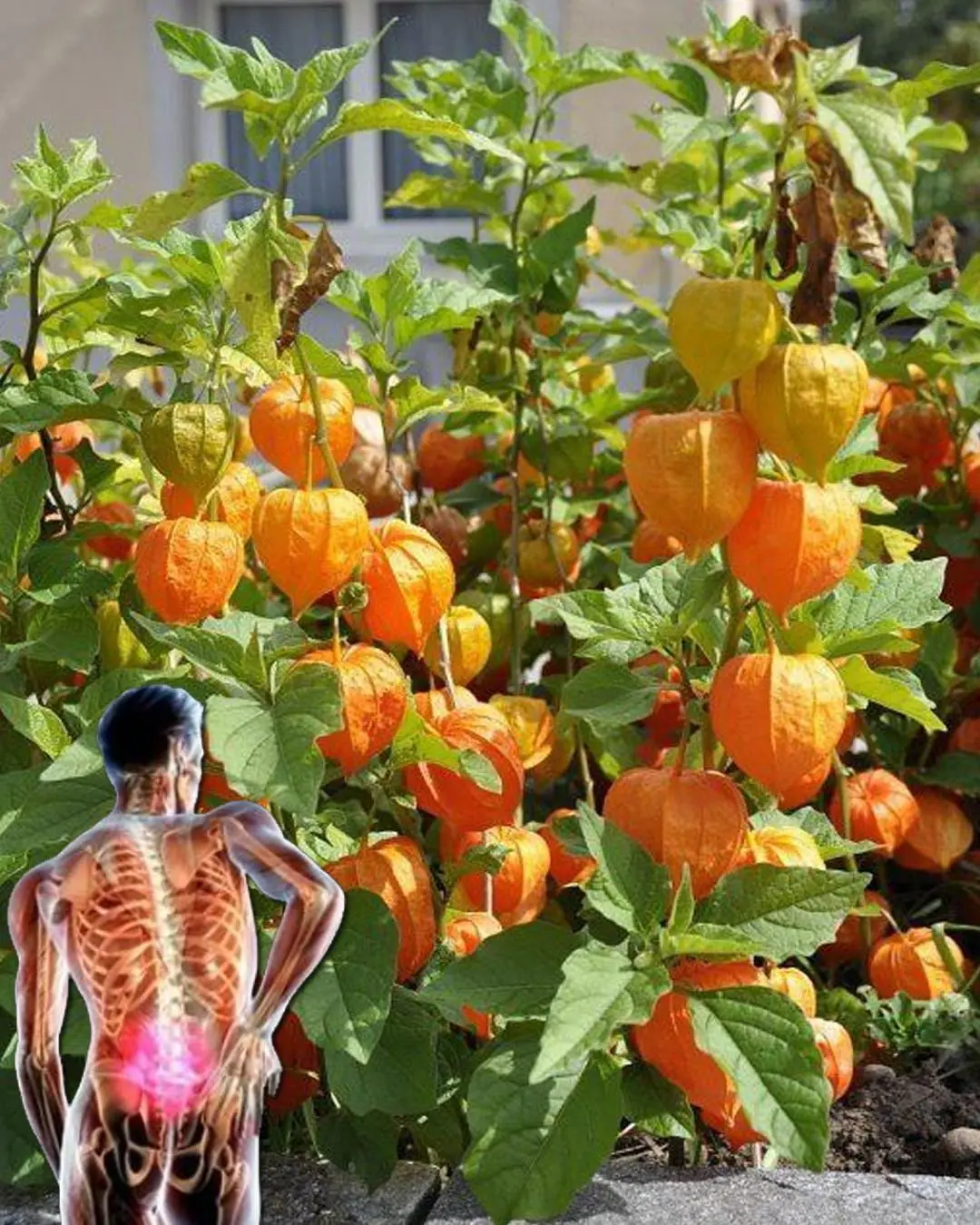

Goldenberries (Physalis peruviana): A Nutrient-Packed Powerhouse for Health and Vision
Garden 08/03/2025 02:21
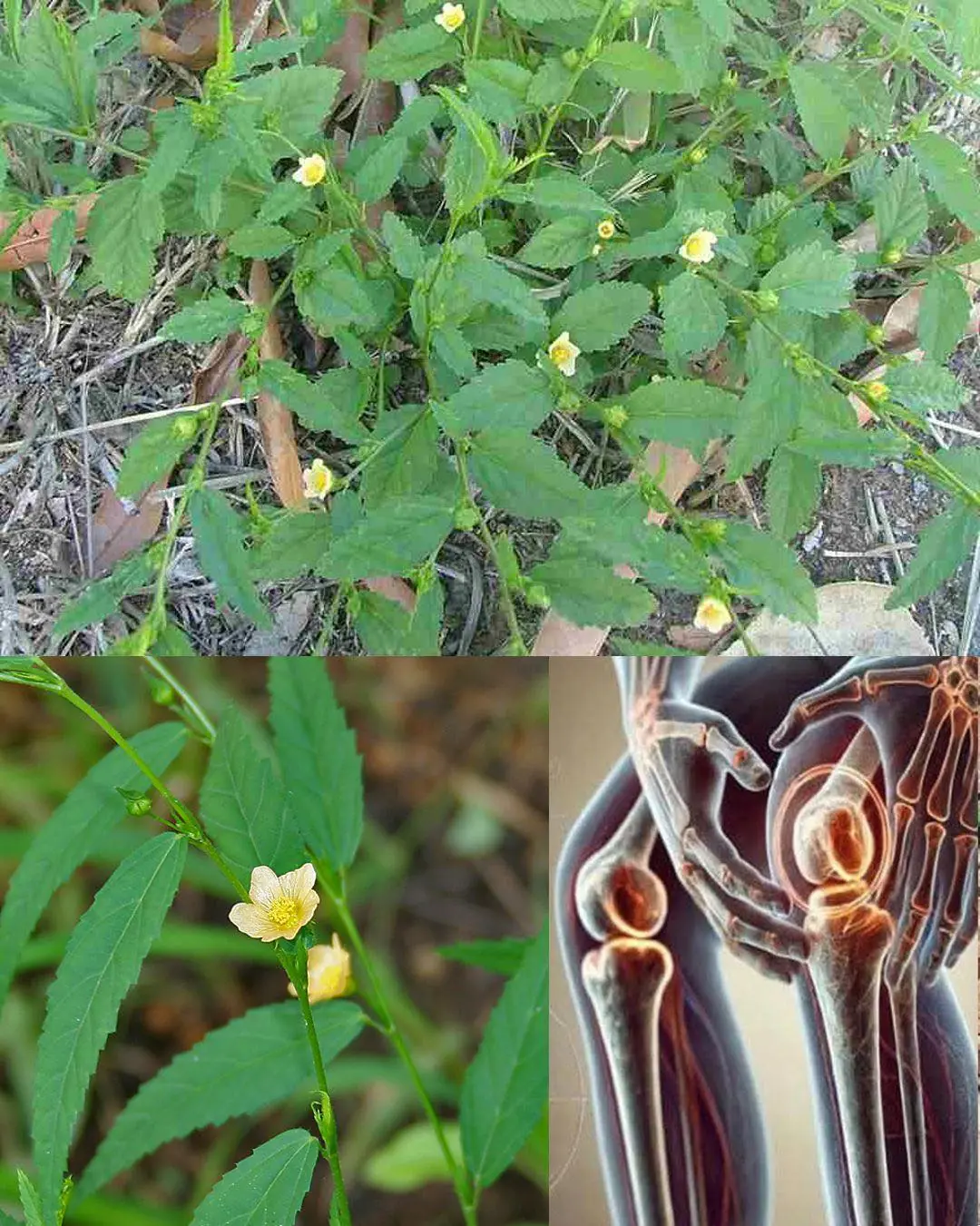

Stubborn Grass: 10 Amazing Benefits & Side Effects
Garden 08/03/2025 02:17

8 Foods You Can Grow in Buckets All Year
Garden 08/03/2025 01:52

So brilliant!
Garden 07/03/2025 18:11
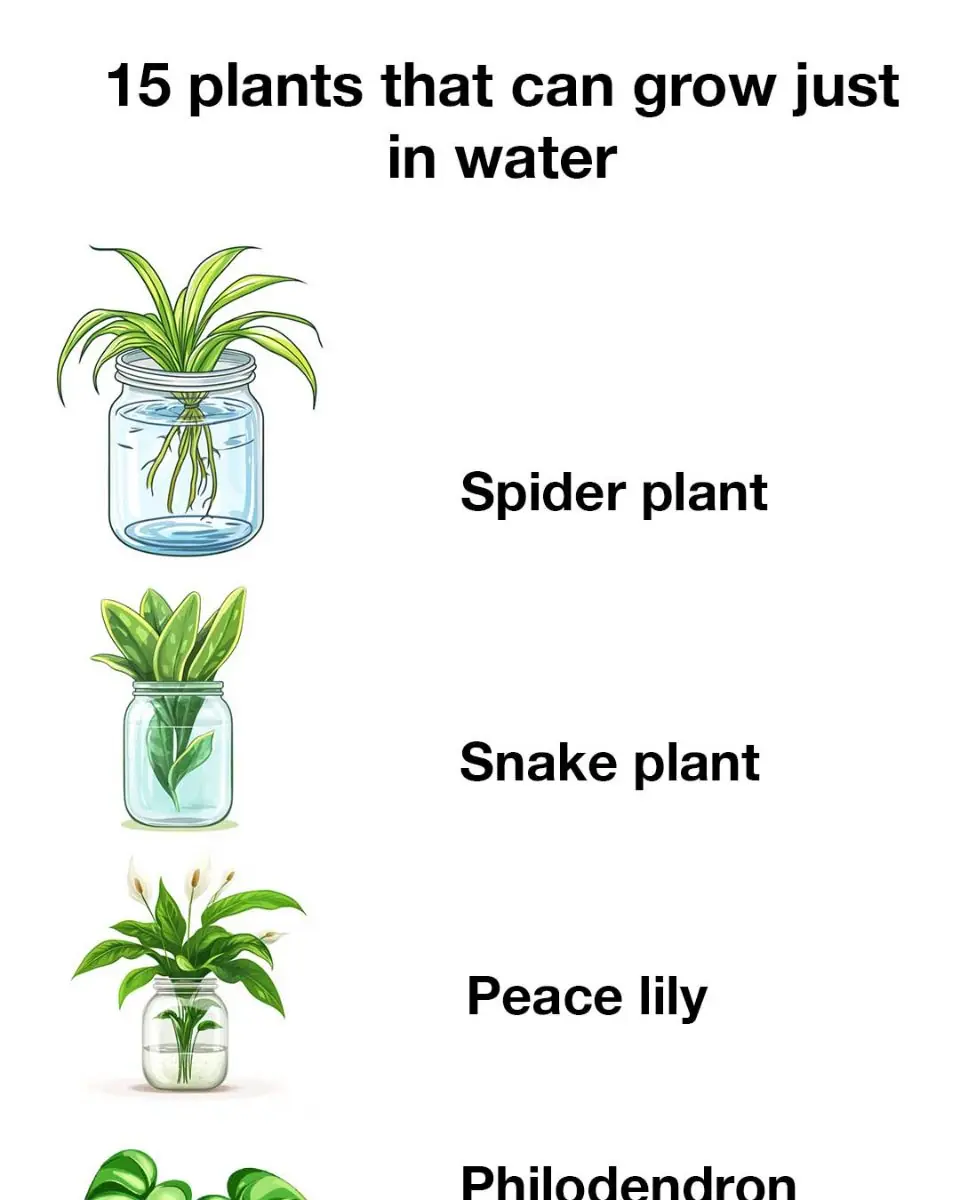
15 plants that can grow just in water
Garden 07/03/2025 15:32

How To Get Peace Lilies To Bloom More Often
Garden 07/03/2025 15:27

12 essential companion planting ideas for raised beds
Garden 07/03/2025 13:17

Plant Once, Pick Forever! 10 Perennial Vegetables You NEED to Plant This Summer
Garden 07/03/2025 02:40

7 Ways How to Attract Hedgehogs to Your Garden
Garden 06/03/2025 02:51
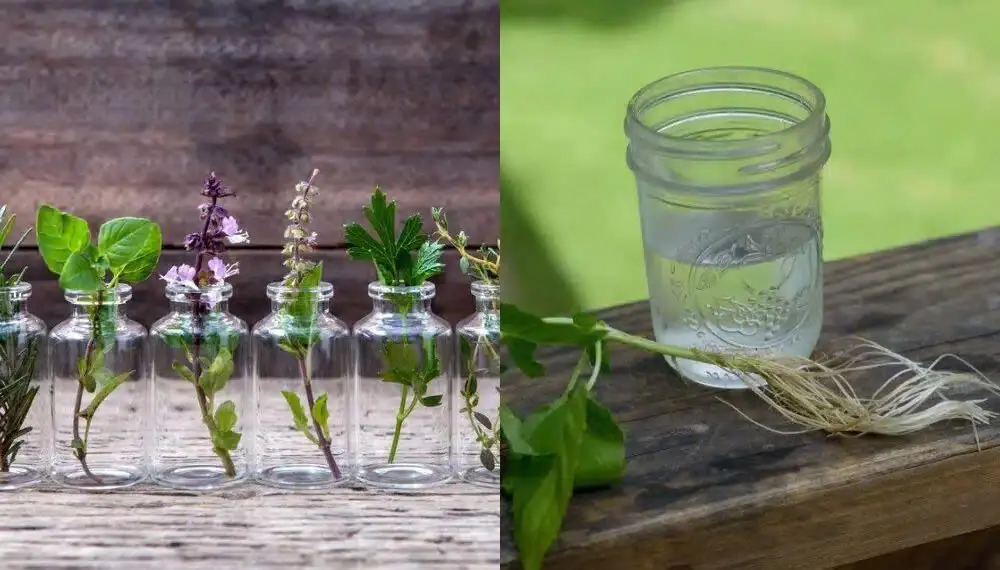
12 Herbs you Can Grow With Just Water all Year Round
Garden 06/03/2025 02:48

20 Perennials That Bloom Multiple Times a Year
Garden 06/03/2025 02:44
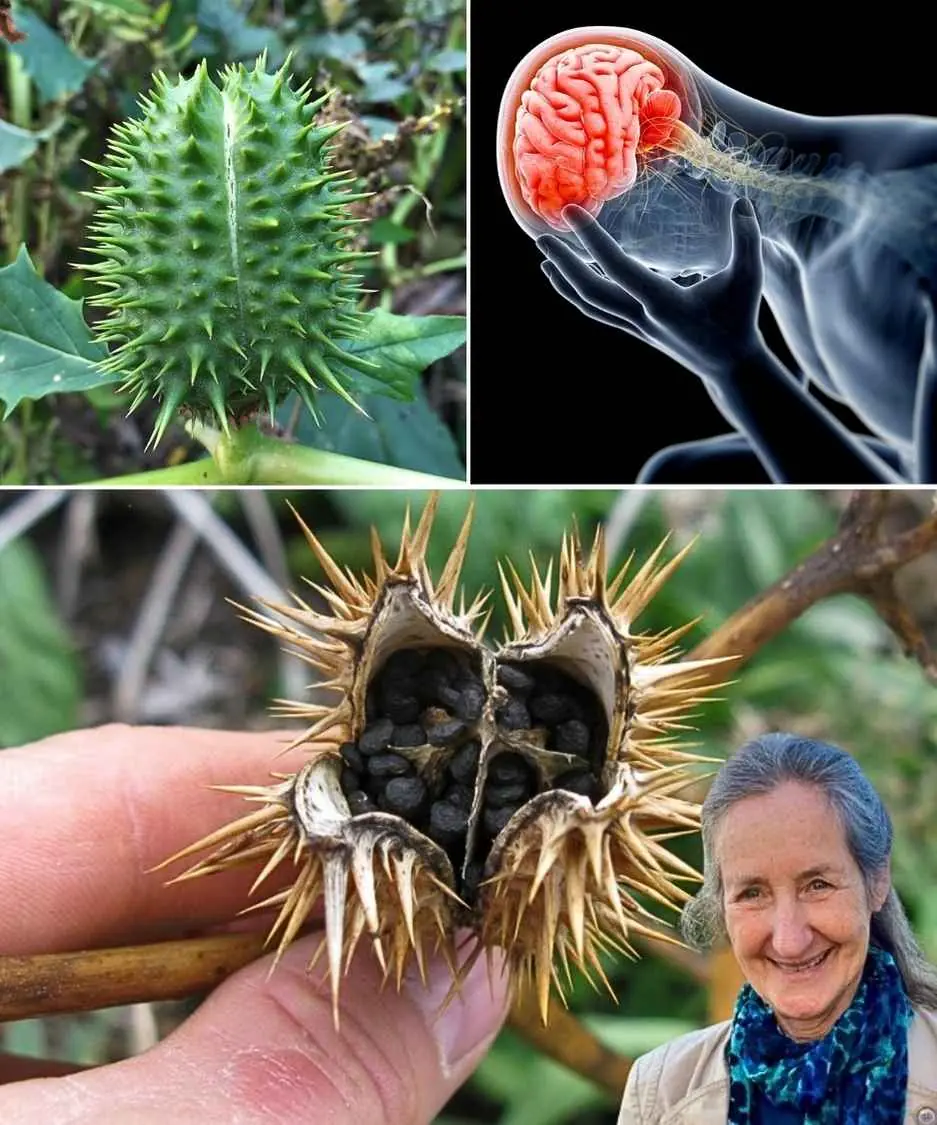

The Hidden Dangers of Datura Stramonium: A Toxic Plant You Should Avoid
Garden 06/03/2025 02:11

20 top gardening hacks of all time
Garden 05/03/2025 23:55

Don’t Discard the Flowers on Your Basil: Here are 8 Ways How to Use Them
Garden 05/03/2025 00:33

This is How to Correctly Plant Tomatoes to Grow 5–8 ft Plants
Garden 05/03/2025 00:26
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more
Fitness 30/10/2025 13:23

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:23
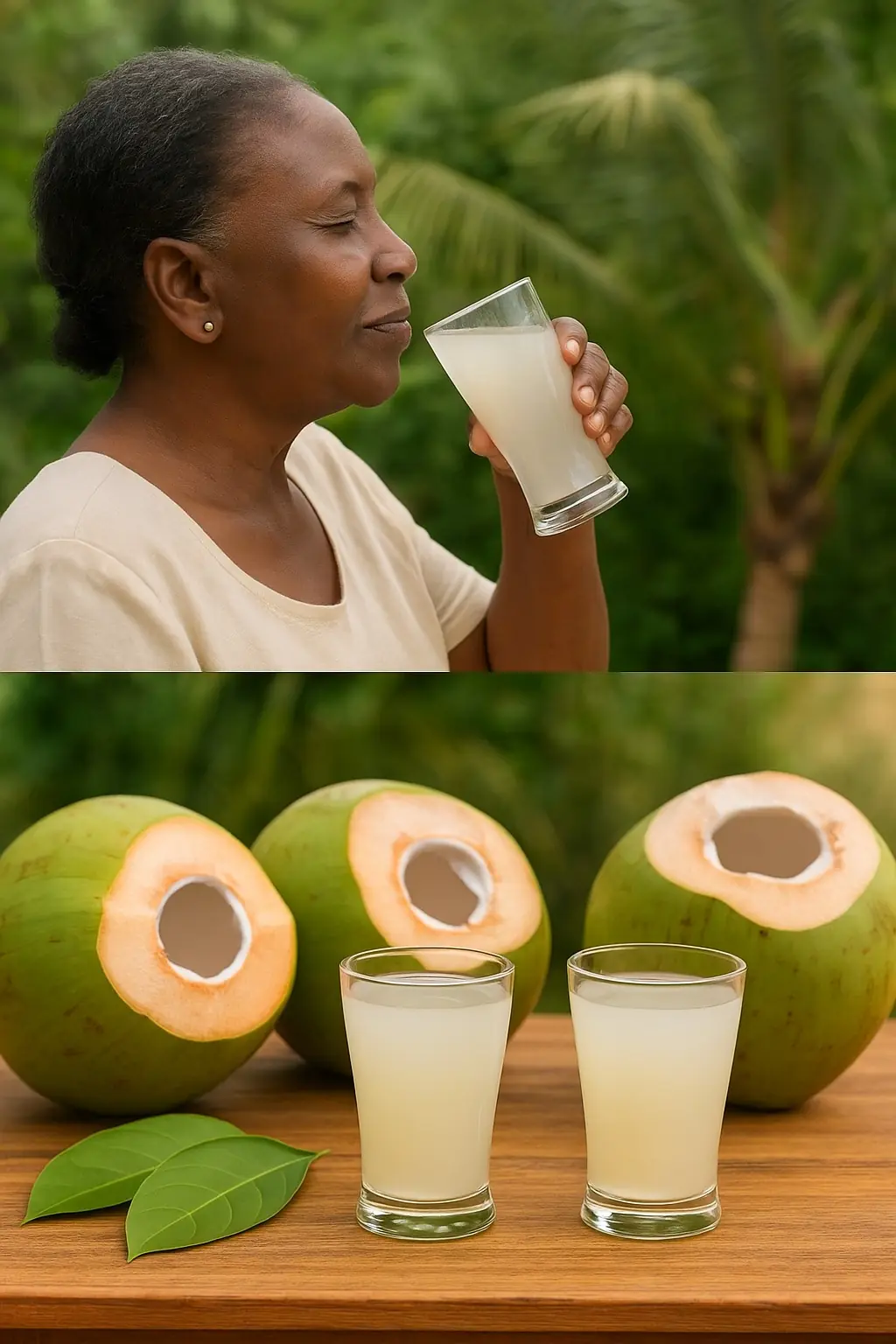

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:21
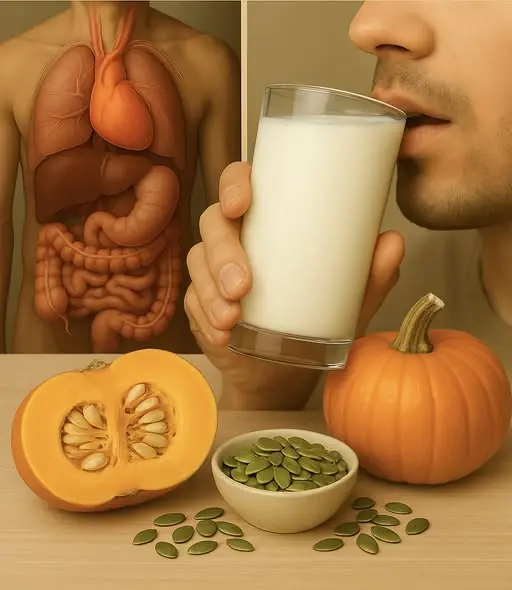

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Healthy 27/10/2025 19:19
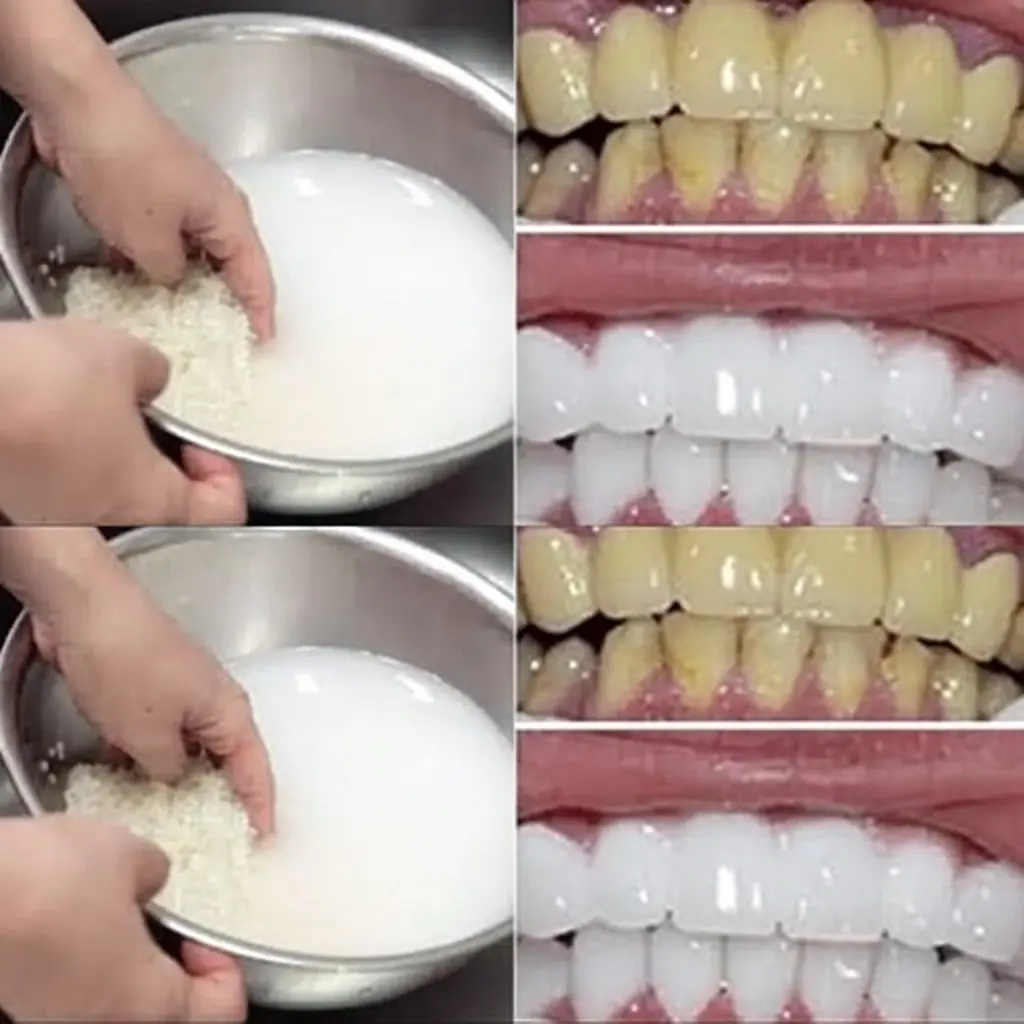
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:42
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:38
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:37

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Healthy 26/10/2025 22:35
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:06
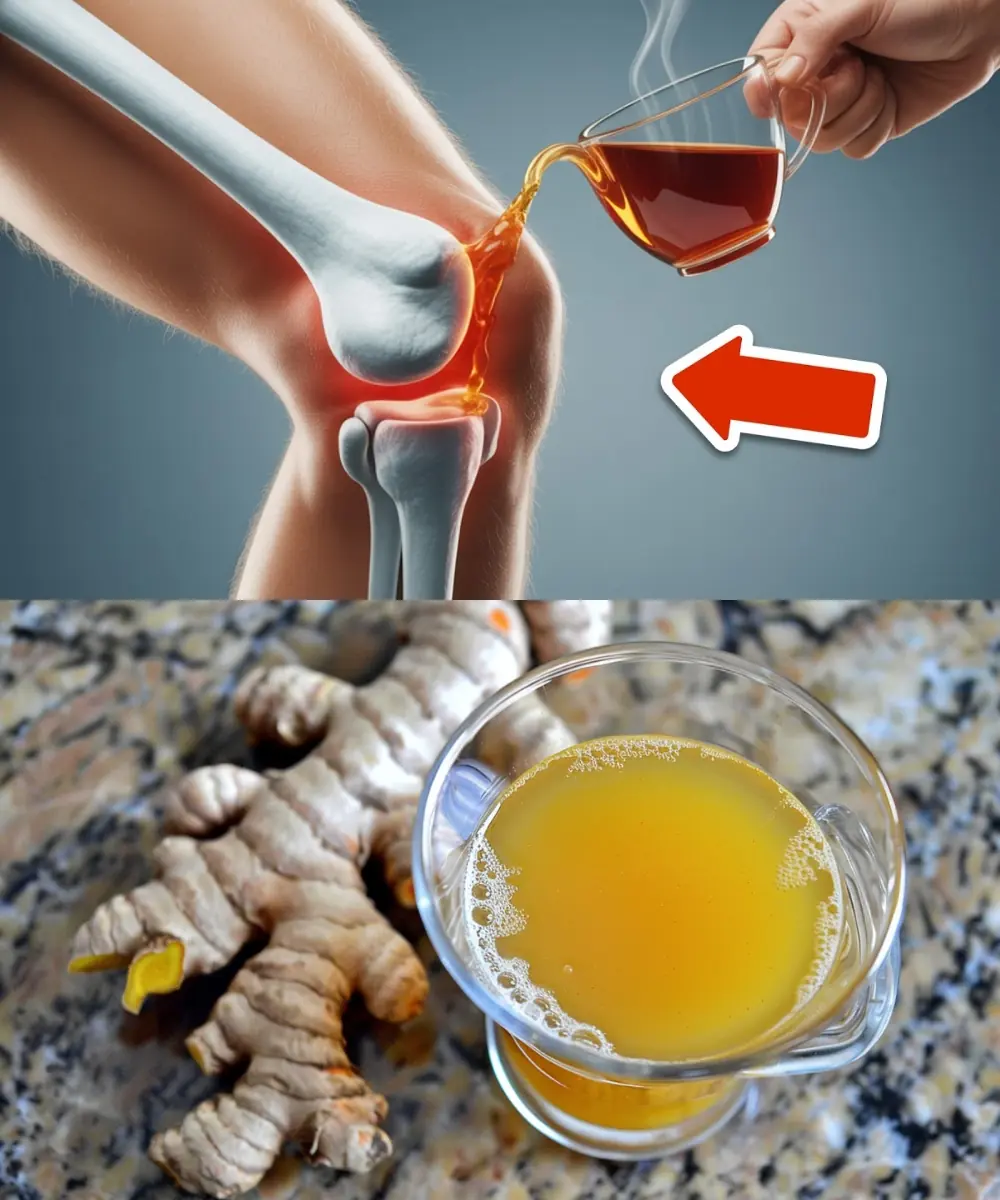

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:04

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe
Healthy 26/10/2025 19:02

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!
Health News 26/10/2025 01:57

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them
Health News 26/10/2025 01:54

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
Health News 26/10/2025 01:44

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You
Fun Fact 26/10/2025 01:36
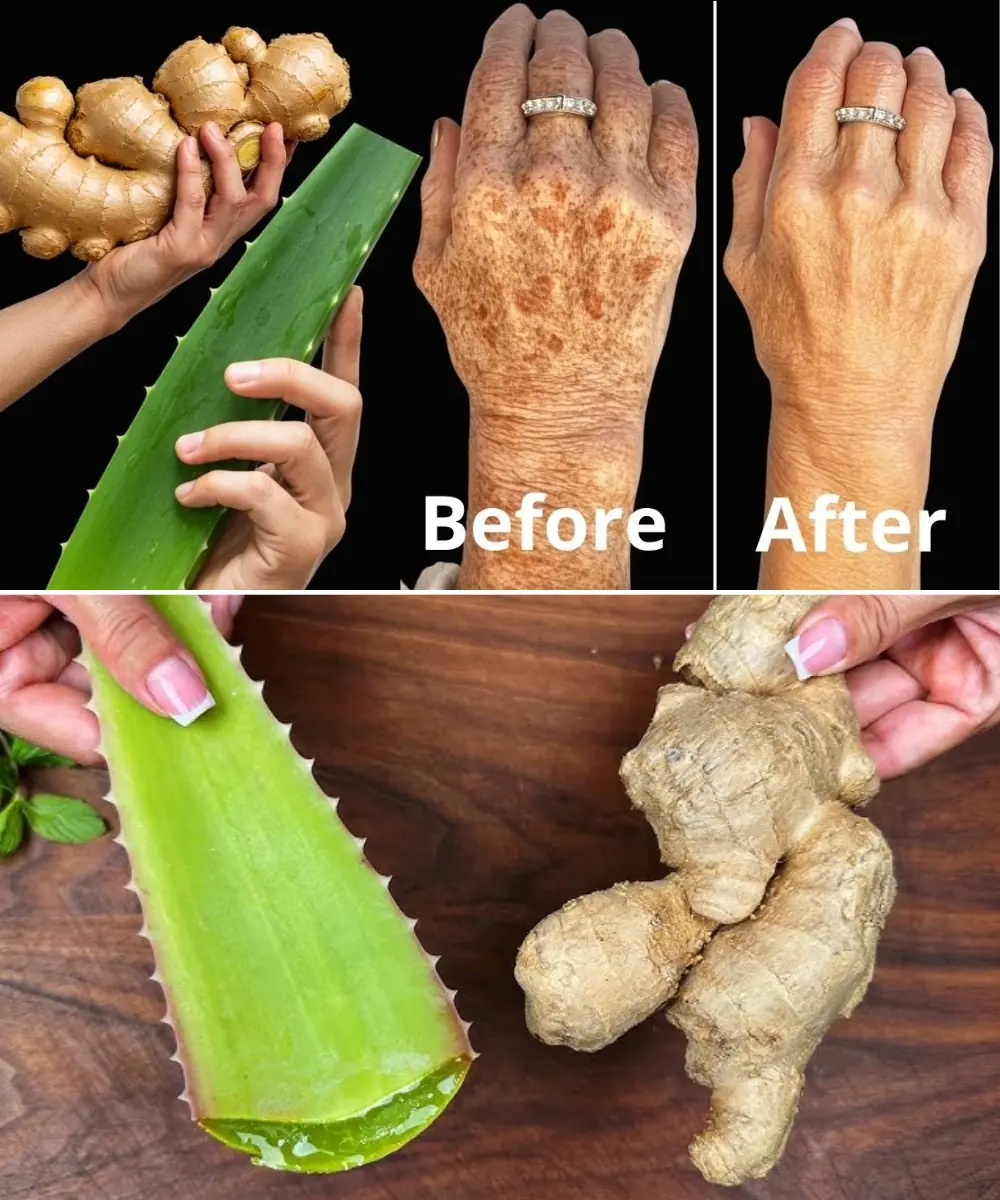

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:44
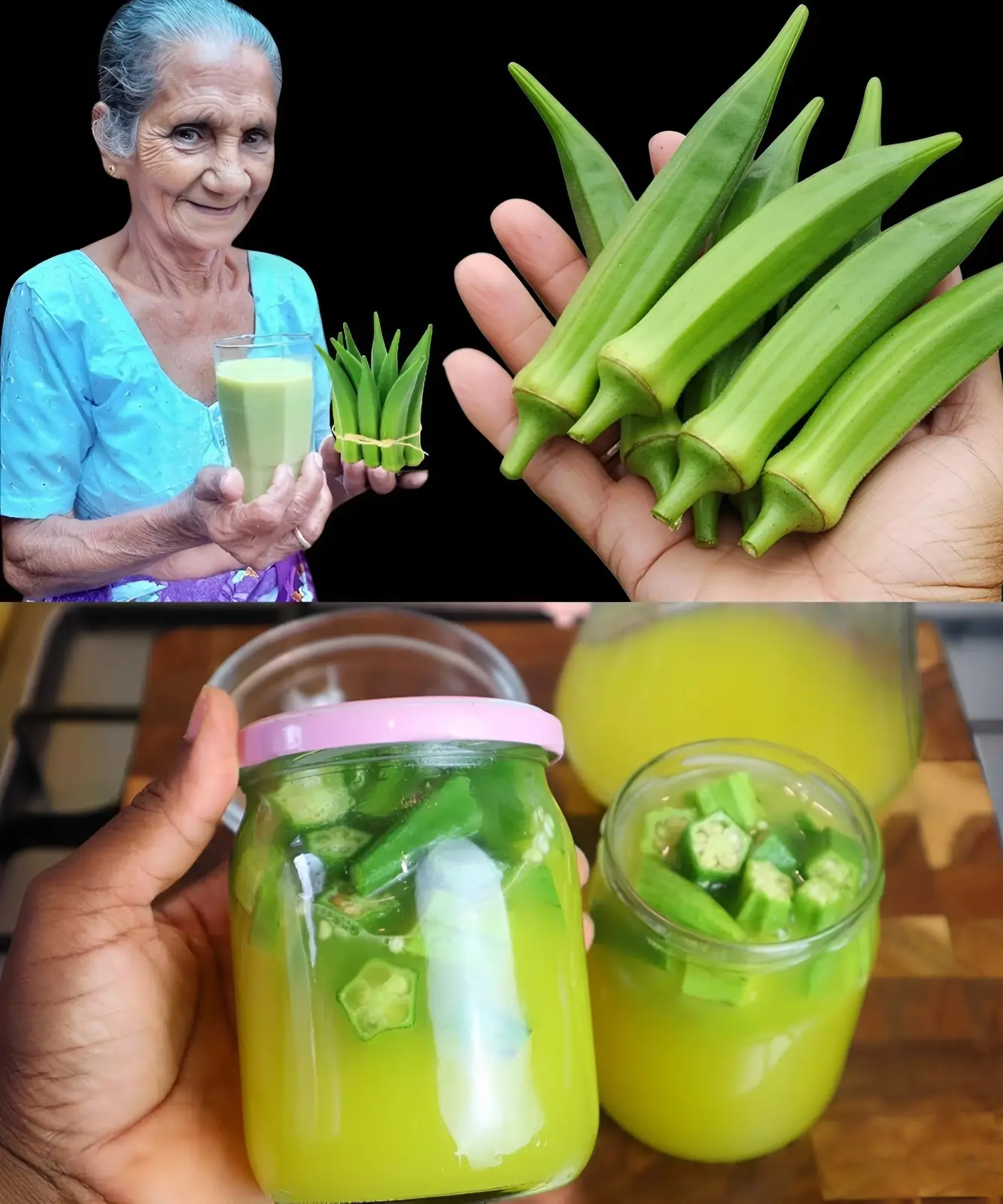

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:42
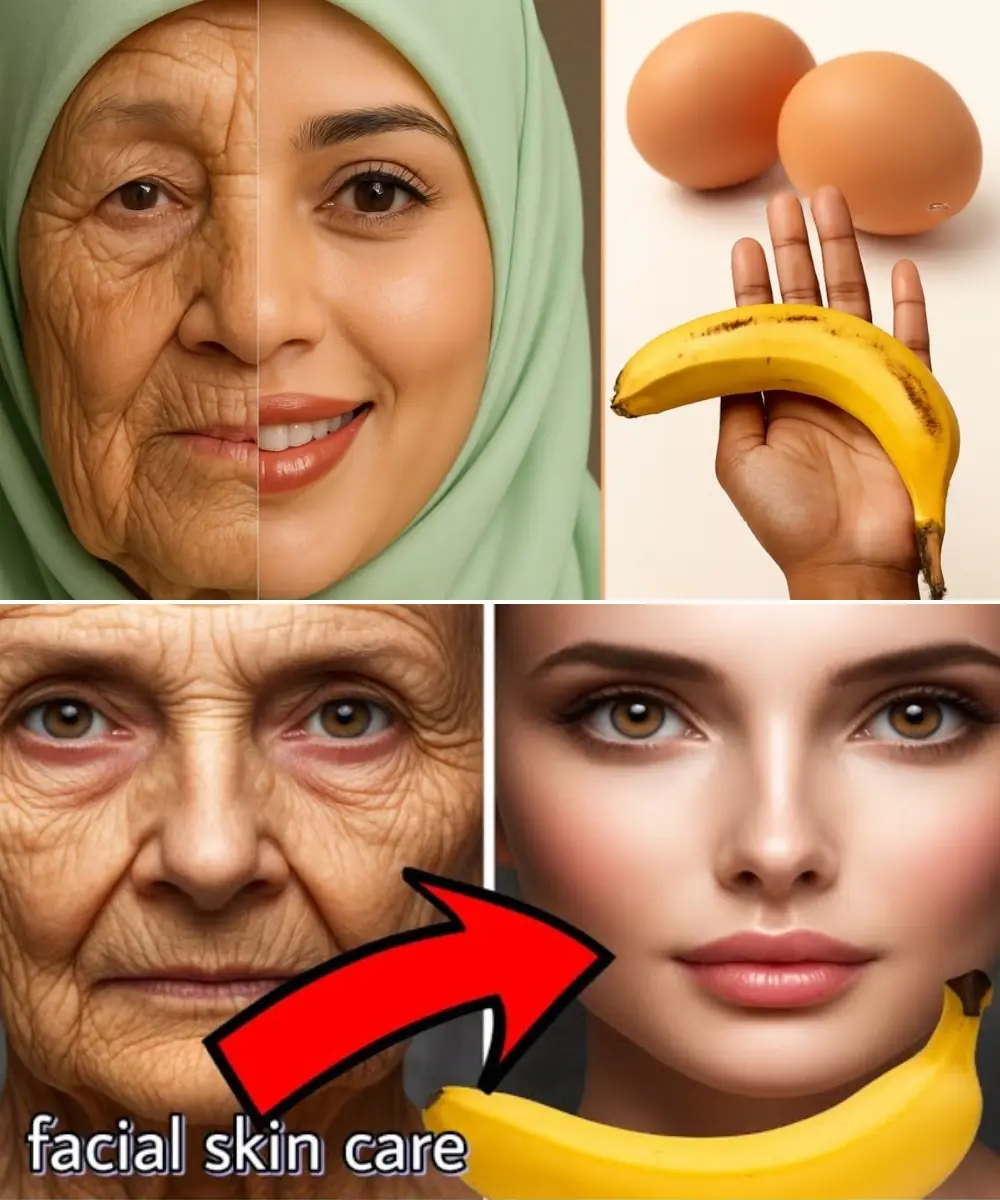

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:29
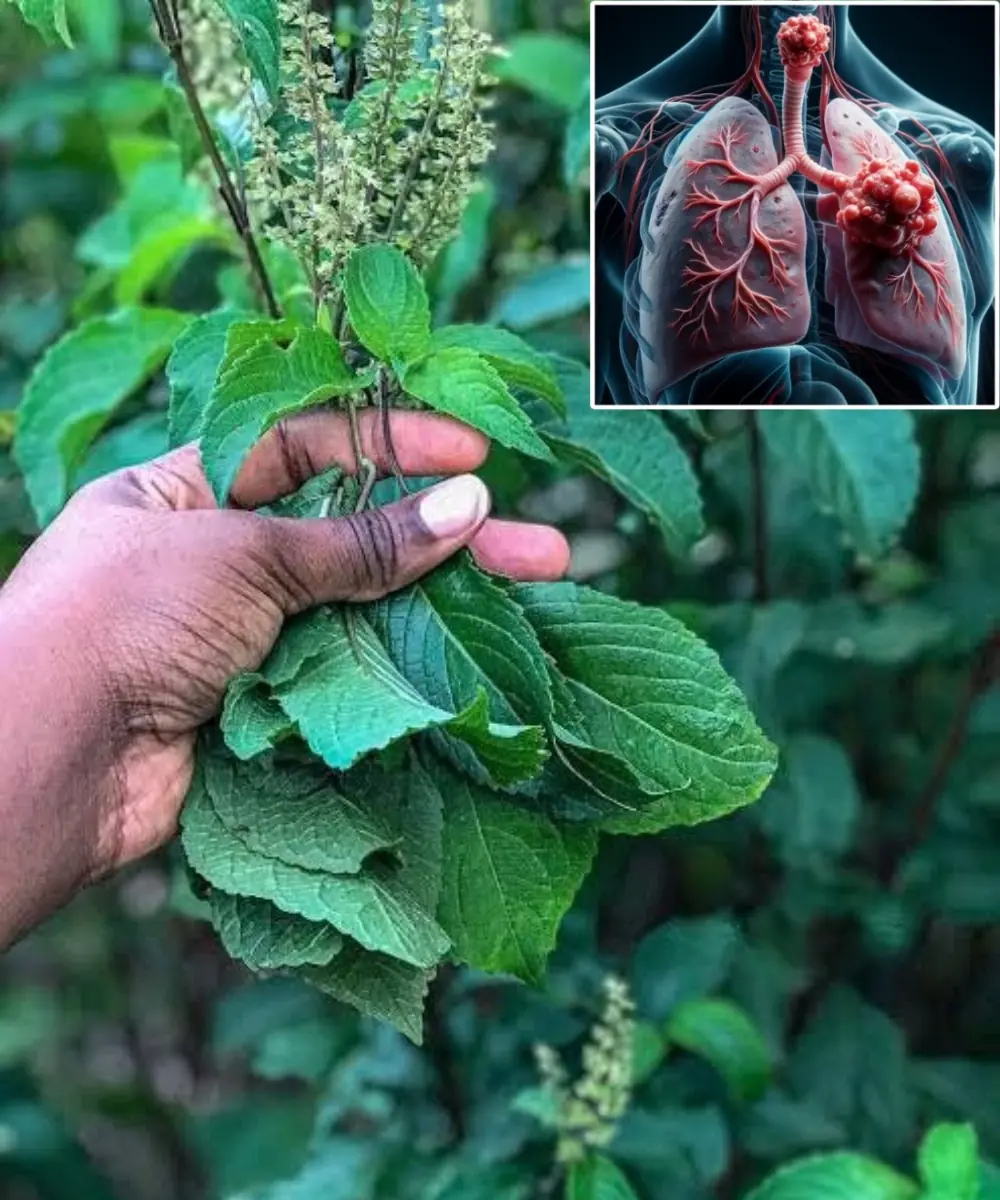

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:24

From White Hair to Black Hair Naturally in Just 5 Minutes — Fast Hair Growth Remedy
Healthy 25/10/2025 19:22
