
How to Prevent Angina? Three Key Factors to Keep in Mind, with Medication as the First Priority
Angina is a common coronary artery disease, primarily affecting middle-aged and elderly individuals. As people age, their bodily functions gradually decline, leading to a weaker immune system and an increased risk of developing angina.
During an angina attack, patients often experience chest pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting, with episodes frequently occurring at night. This makes it crucial to monitor any physical changes while sleeping and take necessary precautions.
Several factors contribute to the onset of angina, including environmental changes and personal health conditions. Therefore, prevention is of utmost importance. To reduce the risk of angina, paying attention to the following three key aspects is essential.
1. Taking Medication Regularly and as Prescribed
For individuals diagnosed with angina, consistent and correct medication use is vital for managing the condition. After identifying the cause, doctors prescribe medications tailored to the patient’s condition. Following the prescribed dosage and schedule is crucial for alleviating angina symptoms and ensuring overall heart health.
Patients must also adhere to dietary restrictions while on medication. It is advisable to avoid spicy, excessively cold, or highly stimulating foods, as these can interfere with the effectiveness of the treatment. Sticking to the prescribed dosage—neither exceeding nor reducing it—is necessary for optimal health outcomes.
2. Maintaining a Balanced and Nutritious Diet
A well-functioning body relies on proper nutrition to fuel its physiological activities. A balanced diet is essential for sustaining energy levels and supporting overall health.
Angina patients should prioritize a light, nutritious diet that includes adequate intake of essential nutrients such as protein, healthy fats, and dietary fiber. High-fat foods should be minimized as they contribute to high cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Hydration is also critical. Drinking enough water aids digestion, facilitates the elimination of waste, and prevents toxin buildup. However, carbonated and highly stimulating beverages should be avoided, as they can negatively impact medication effectiveness and worsen the condition.
3. Establishing Healthy Sleep and Lifestyle Habits
With increasing work and life pressures, working overtime has become a norm for many people. However, prolonged periods of high-intensity work can lead to chronic fatigue, a significant risk factor for angina.
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and avoiding late nights are crucial for heart health. Chronic sleep deprivation and overwork elevate the risk of sudden cardiac events and worsen angina symptoms. It is highly recommended that angina patients develop regular sleep habits by going to bed early and waking up early. Incorporating moderate physical activity into daily routines can further enhance cardiovascular resilience and reduce the likelihood of disease progression.
Conclusion
Preventing angina requires a combination of regular medication, a balanced diet, and a healthy lifestyle. By taking proactive steps such as adhering to prescribed treatments, eating nutritious foods, and maintaining proper sleep habits, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of angina attacks and improve their overall well-being. Small, consistent changes in daily habits can make a big difference in heart health.
News in the same category


Why is it said that warm lemon juice can save a life: Drinking it at the right time will prevent cancer, filter blood, and remove belly fat
Doing This for One Hour a Week Can Slow Cancer Progression
U.S. Develops "Smart Bomb" to Eliminate Metastatic Cancer
Discovery of a "Checkpoint" Affecting 70% of Cancer Types
Scientists Have Found an Effective Cancer Treatment Solution

6 Amazing Benefits of Drinking Okra Water with Lemon Every Morning

What Happens When You Drink Lemon Turmeric Water Every Morning?

9 Out of 10 People Suffer from Back Pain? These 3 Foods Can Help Detox Your Body and Relieve Discomfort

What Happens When You Stay Up Late Scrolling on Your Phone? The Harsh Truth: 4 Consequences Your Body Will Pay For

12 Superfoods to Balance Hormones and Preserve Youth—Some Are Surprisingly Affordable!

Can Your Face Reveal Your Lifespan? Four Facial Features of Long-Lived People—Do You Have Them?
Let me make it clear: Cancer patients can boost their immune system through regular exercise, but there are six key points to keep in mind.
Uterine Fibroids: Four Key Symptoms Women Should Watch For
Why Some Doctors Advise Against Brain CT Scans? Essential Facts You Should Know

Why Are Heart Attacks Becoming More Common in Young People? Three Habits You Should Avoid
4 Signs Your Body May Be Lacking Vital Energy and Blood – Here’s What to Do About It
Osteoporosis Myths You Need to Stop Believing – Are You at Risk?
If you have cirrhosis, you should pay more attention to your diet. Only by following these guidelines can you improve your condition.
News Post

Excessive consumption of green juices can cause oxalate kidney injury.
10 Ways To Support Your Lymphatic System

Pure Magic: Burning a Clove of Garlic, What Happens After 15 Minutes at Home?
The Juice That Strengthens Bones and Soothes Knee Pain Naturally
Clean Your Kidneys, Liver & Lungs – Powerful Natural Detox! 🍊🌿

Euphorbia Hirta: Nature's Remedy for Respiratory and Immune Health

Why is it said that warm lemon juice can save a life: Drinking it at the right time will prevent cancer, filter blood, and remove belly fat

Scandalous discovery of why intimate parts smell like fish

First childhood death from measles reported in the US amid active outbreak.
If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, the Body Will Show these 10 Signs
10 Foods That You Should Eat Daily For Clean Arteries

Natural Recipe with Watermelon, Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger

10+ Foods to Help Lower Your Blood Sugar

5 Types of Foods That Naturally Contain Progesterone – Doctor’s Advice: Women Over 45 Should Eat More
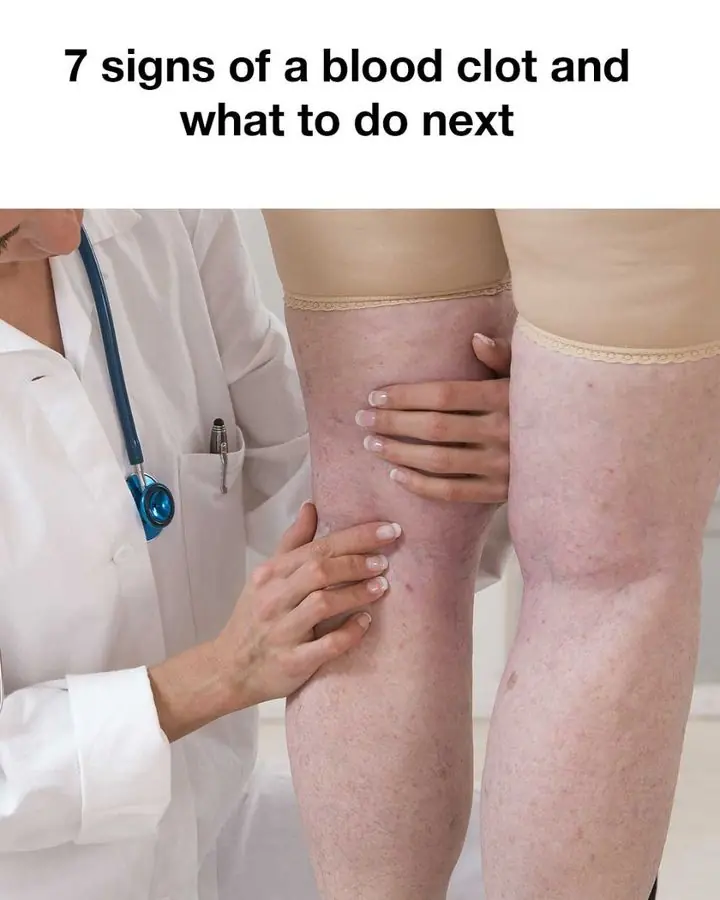
So useful! Gonna watch out for these Holly Owens Contributing Writer
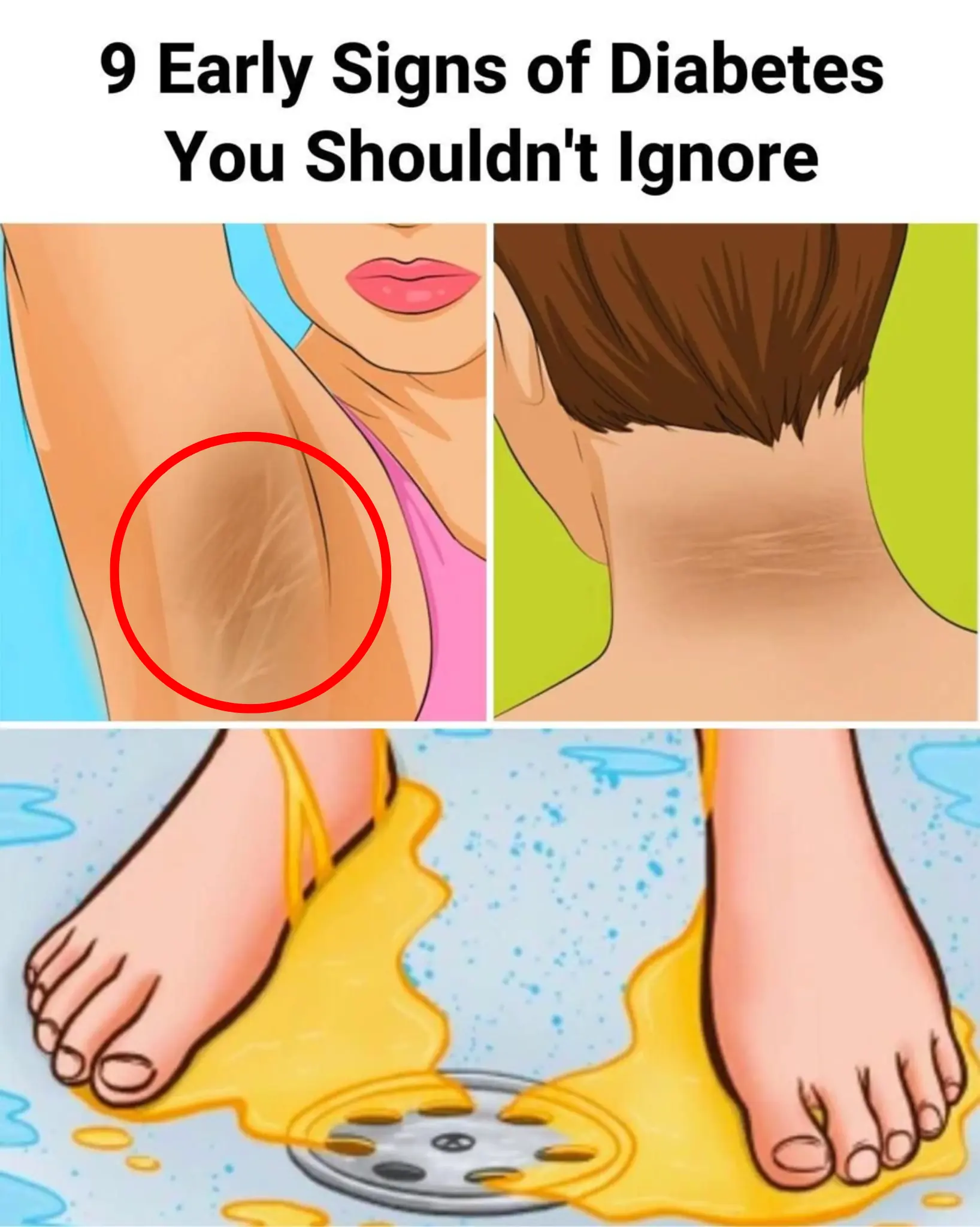
9 Early Signs of Diabetes You May Not Be Noticing
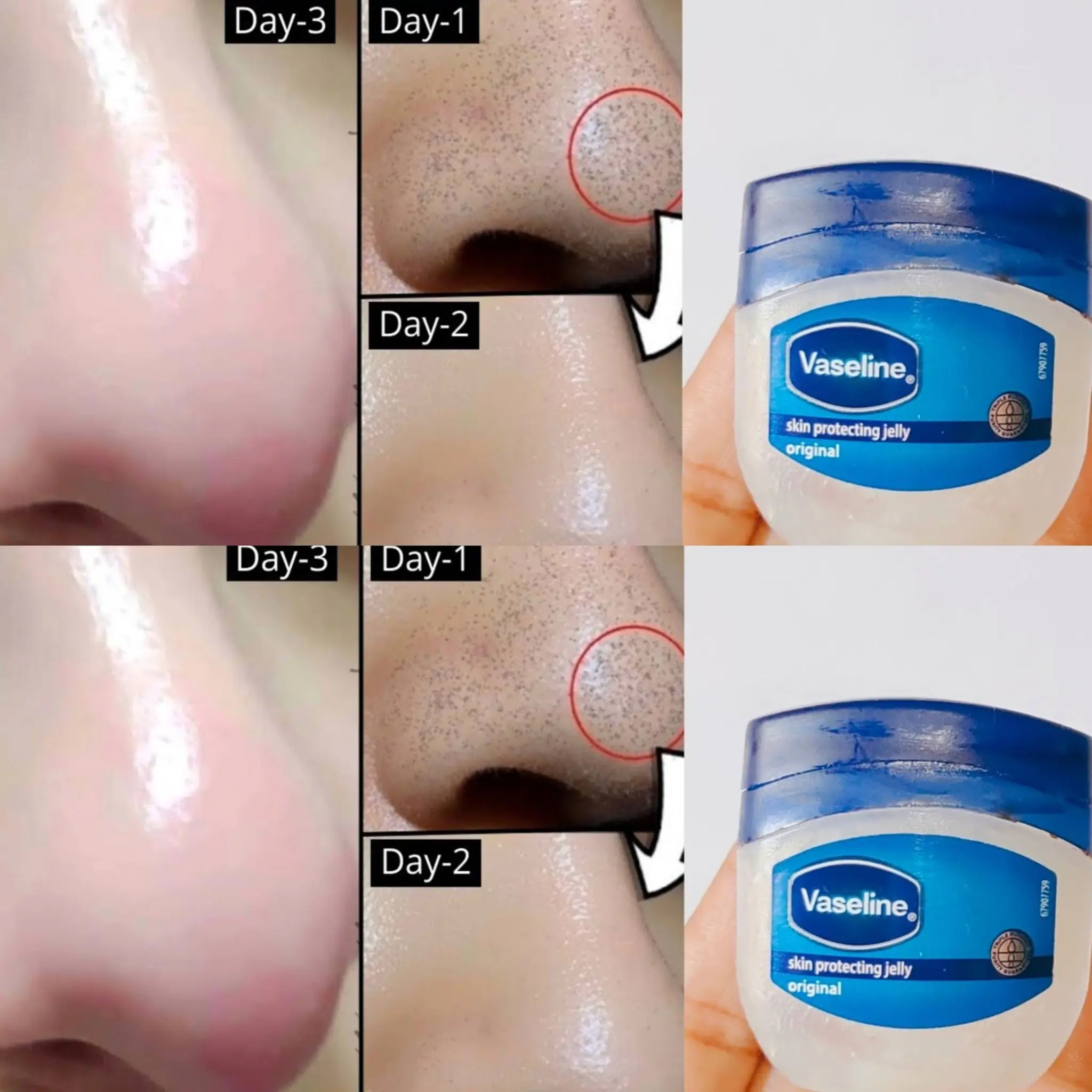
How to Remove Blackheads and Whiteheads Naturally with Vaseline
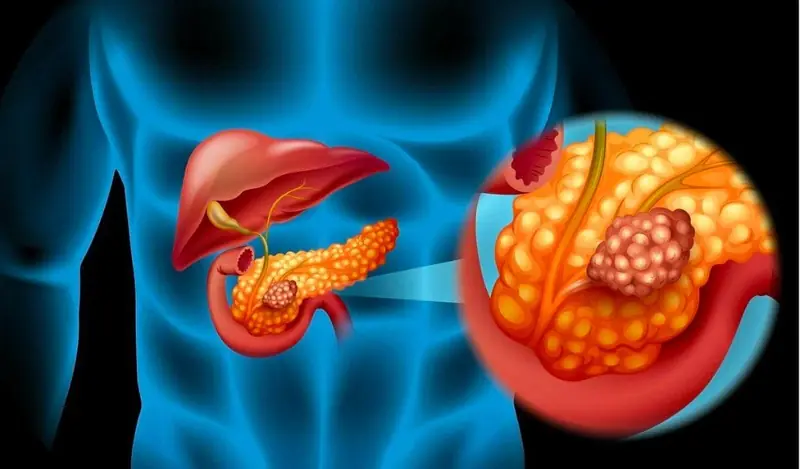
What Happens When Pancreatic Cancer Is Caused by Diet? Doctors Warn: People with a Weak Pancreas Should Avoid These Foods

Mix Avocado Seed with Turmeric and Cinnamon
