
Study Reveals Rising Cancer Rates Among Gen X and Millennials Compared to Older Generations

Recent studies have highlighted a concerning trend: cancer diagnoses are increasing among younger populations, particularly among Generation X and Millennials. This rise encompasses 17 specific cancer types, with researchers pointing to factors such as environmental toxins, dietary habits, and obesity as potential contributors. However, further research is necessary to fully understand the underlying causes.
Key Findings: Escalating Cancer Rates in Younger Populations
While previous studies suggested an uptick in certain cancers among younger individuals, recent research has delved deeper by analyzing cancer incidence and mortality rates by birth year. The findings indicate that early-life exposure to carcinogenic factors significantly elevates cancer risk by age 50. As Generation X and Millennials age, the number of cancer cases within these groups is projected to rise.
17 Cancer Types with Increased Incidence
An analysis of data encompassing over 23.6 million cancer diagnoses and 7.3 million cancer-related deaths between 2000 and 2019 identified 17 cancers with heightened incidence among younger generations:
- Small intestine
- Cardia gastric
- Ovary
- Estrogen receptor-positive breast
- Non-HPV-associated oral and pharynx (in females)
- Liver and intrahepatic bile duct (in females)
- Kaposi sarcoma (in males)
- Anus (in males)
- Colorectal
- Endometrial
- Gallbladder and other biliary
- Pancreas
- Kidney and renal pelvis
- Myeloma
- Non-cardia gastric
- Leukemia
Notable Trends in Incidence and Mortality
Certain cancers, including those of the pancreas, kidney, thyroid, and small intestine, have experienced particularly sharp increases in incidence. Mortality rates have also risen for liver, endometrial, gallbladder, testicular, and colorectal cancers. These trends suggest that the escalating cancer risk is not solely attributable to improved detection methods but reflects a genuine increase across the population.
Potential Factors Driving the Increase
Several factors have been proposed to explain the rising cancer rates among younger individuals:
-
Obesity: Linked to 10 of the 17 identified cancers, obesity rates have surged since the 1970s, especially among those aged 2 to 19.
-
Environmental Pollutants: Chronic exposure to environmental toxins may contribute to increased cancer risk.
-
Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary behaviors and disrupted sleep patterns are known to elevate cancer risk.
-
Western Diet: Diets rich in processed foods, sugars, saturated fats, and refined grains are directly associated with colorectal and breast cancers. Alterations in the gut microbiome, influenced by diet and antibiotic use, may also play a role in the development of digestive system cancers.
Encouraging Developments Amid Challenges
Despite the concerning rise in cancer incidence, there are positive developments. The introduction of HPV vaccinations for women born around 1990 has led to a reduction in cervical cancer rates. Similarly, declining smoking rates have resulted in fewer cases of esophageal, laryngeal, and lung cancers. Advancements in early detection have also contributed to a decrease in overall cancer mortality rates.
This body of research underscores the importance of addressing contemporary health challenges to combat the rising cancer rates among younger populations. While Generation X and Millennials face increased risks for certain cancers, proactive lifestyle changes, preventive measures, and medical advancements are making a positive impact. By comprehending the factors driving these trends, society can work towards reducing future cancer incidence and improving outcomes for younger generations.
News in the same category


If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain
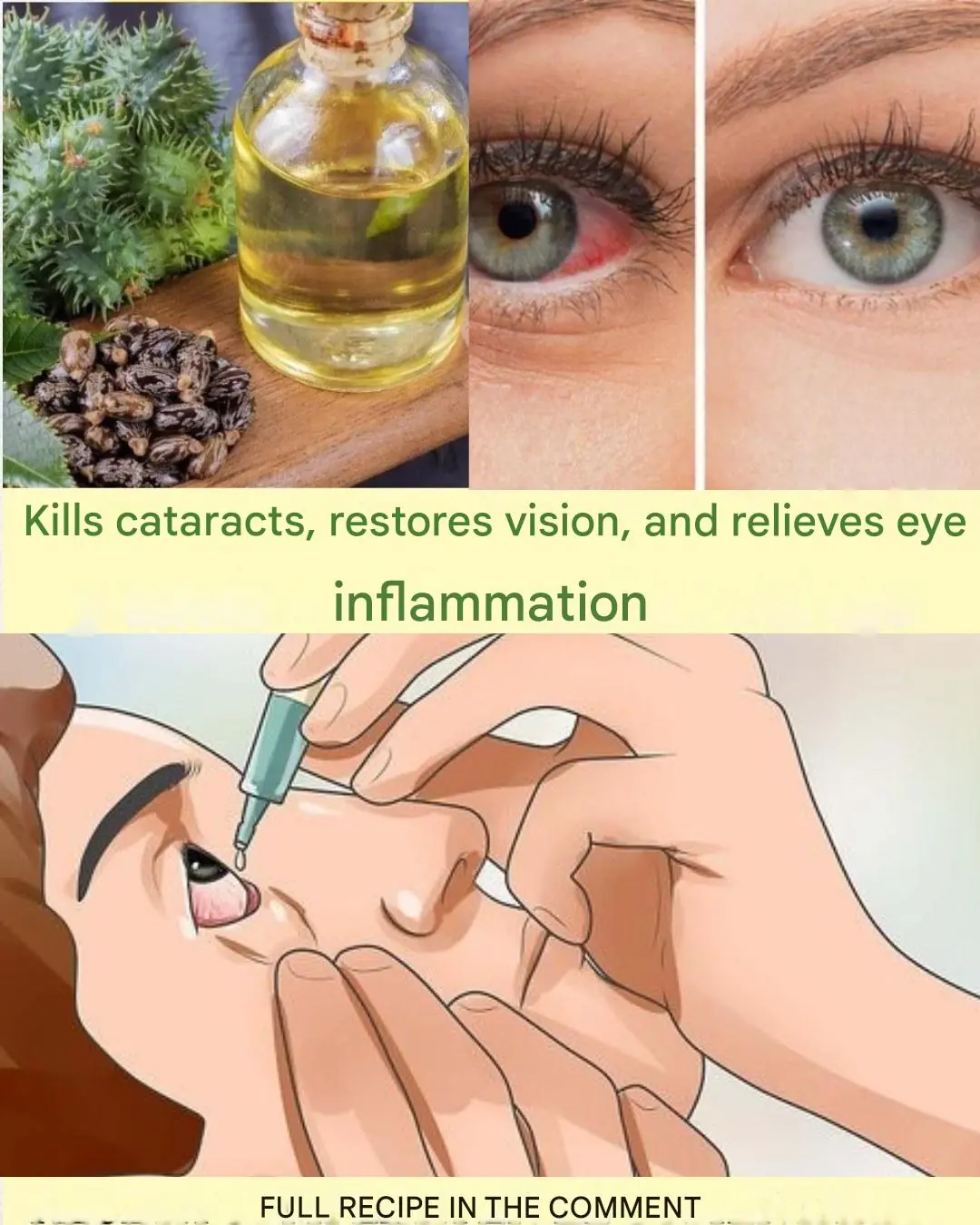
Natural Remedy for Cataracts and Eye Inflammation: Restore Your Vision Naturally

Unlock the Golden Magic of Corn Silk Tea
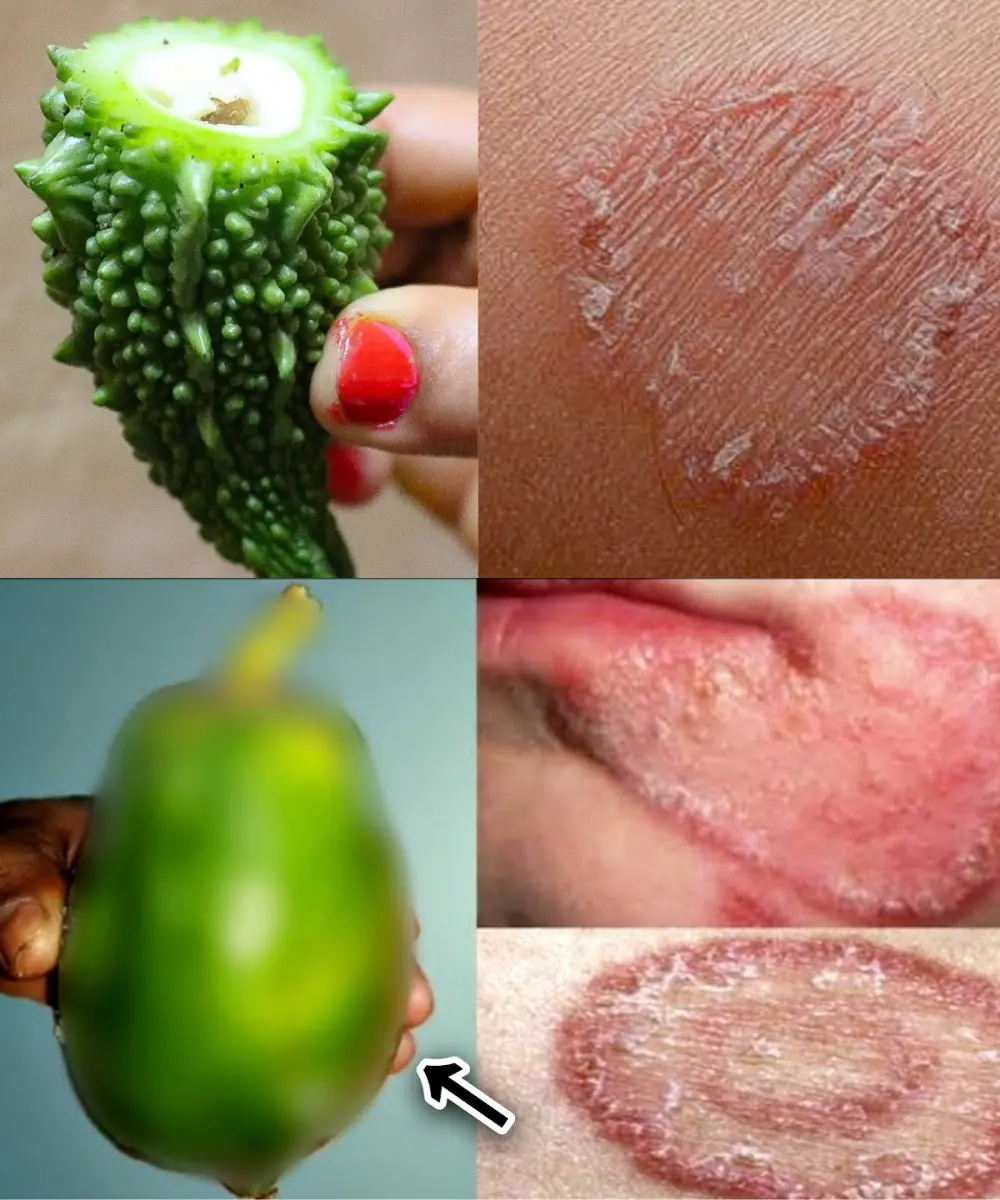
9 Powerful Home Remedies to Get Rid of Fungal Infection (Daad, Khaj, Khujli) Fast
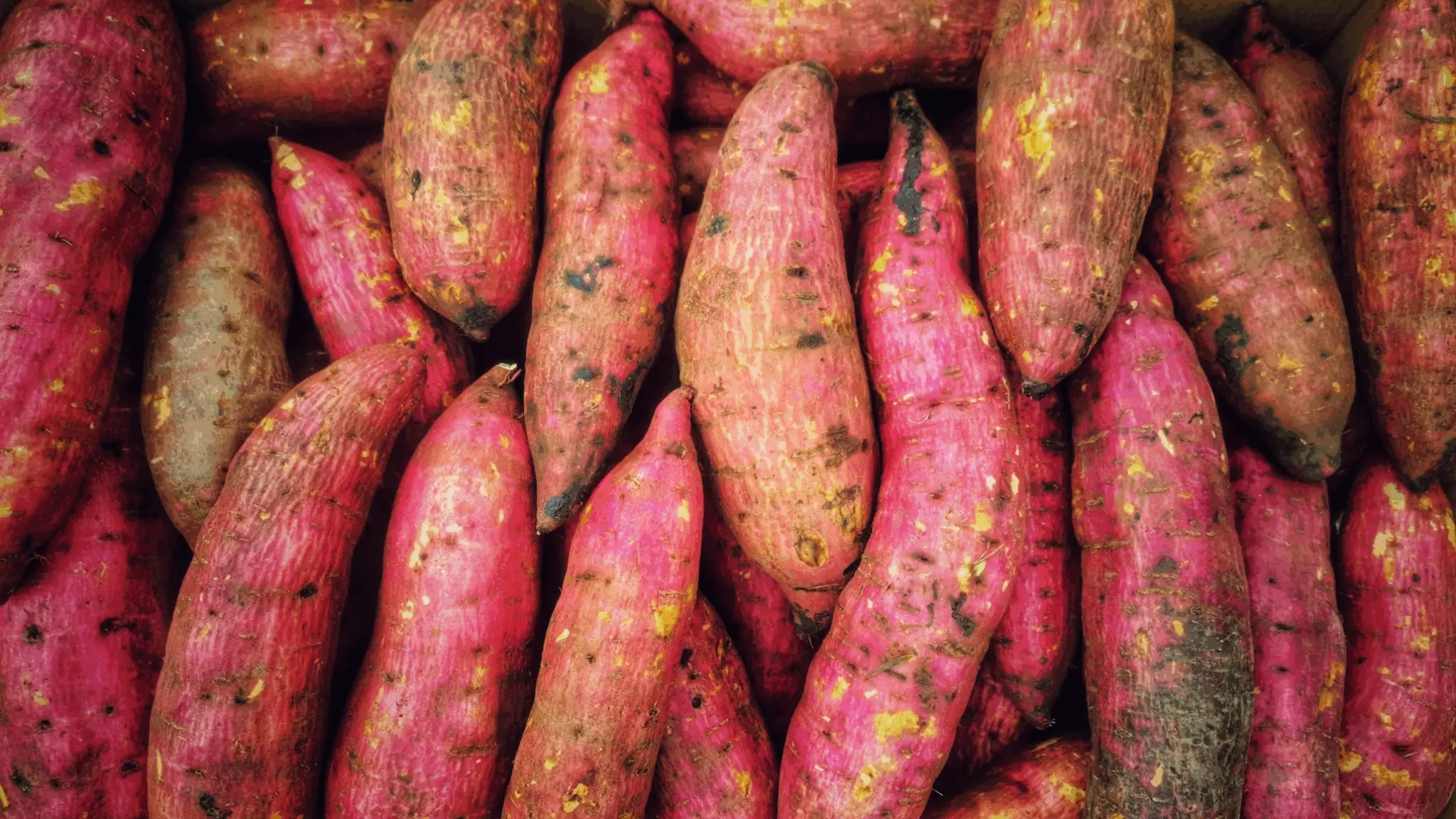
7 Shocking Health Benefits Of Eating Sweet Potatoes Every Day — According To Science

About 15 Minutes Before a Stroke, the Body Often Sends 4 Clear Warning Signs — Call Your Loved Ones Immediately
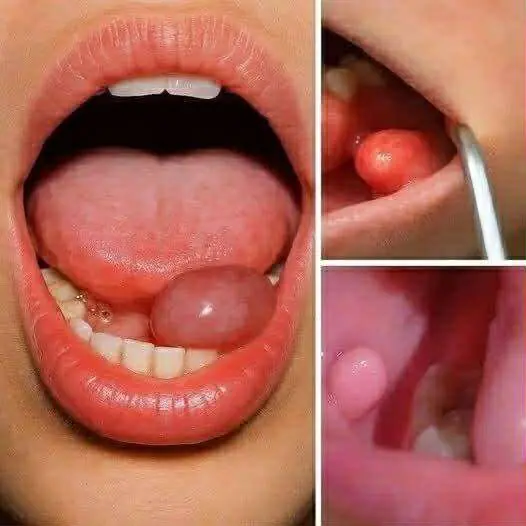
Hidden Dangers in Your Mouth: Early Signs of Oral Cancer

The Secret Power Of The Herb That Helps You Age Gracefully

The Unexpected Benefits of Eating Chicken Feet
If You See Someone with “Blue Veins,” Tell Them This — It Could Save Their Life
The Secret Power of Two Eggs a Day: Could This Simple Habit Transform Your Health? Buy vitamins and supplements

Man Passed Away After Eating Eggs — Stop Eating Eggs This Way Immediately
8 Foods That Fight Tumors — Eat Them Regularly

Does Eating Bananas Before Bed Have Any Benefits?

The Tongue as a Health Indicator: Meaning of a Whitish Color

Benefits of Boiled Eggs: Nutrition and Healthy Recipes
5 early warning signs of cervical cancer
7 Innocent Mistakes That Get Your Kidneys in Big Trouble
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
