
Understanding Benign Lymph Nodes: Key Indicators and When to Seek Medical Advice
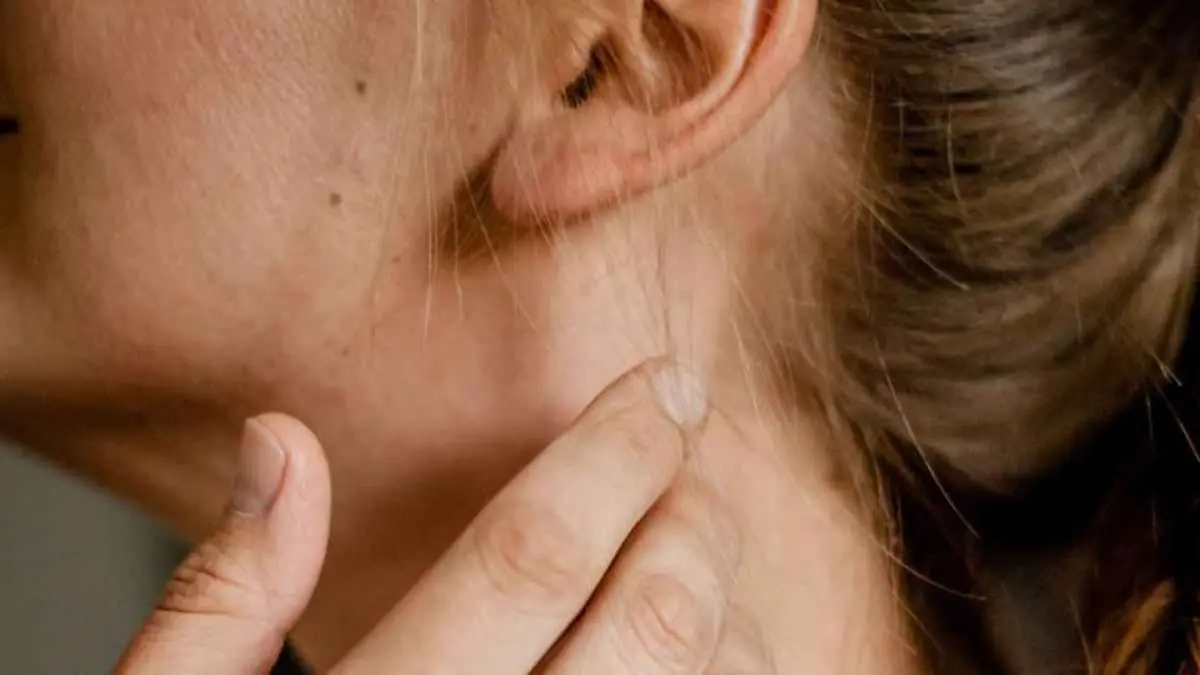
Benign lymph nodes, small bean-shaped structures distributed throughout the body, play a crucial role in the immune system by combating infections. Occasionally, individuals may notice swollen or palpable nodes, especially when the body is responding to infections. Recognizing the characteristics of benign lymph nodes and differentiating them from malignant ones is essential for appropriate health management.
What Are Benign Lymph Nodes?
Benign lymph nodes are non-cancerous enlargements of the lymphatic glands. Swelling often indicates an active immune response to infections, with nodes increasing in size as they work to filter out harmful pathogens.
Common Causes of Benign Lymph Node Swelling
Swollen lymph nodes are typically a response to infections caused by bacteria or viruses. Common causes include:
-
Common Infections:
- Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Measles
- Ear infections
- Dental abscesses
- Mononucleosis
- Skin infections like cellulitis
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
-
Uncommon Infections:
- Tuberculosis
- Sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis
- Toxoplasmosis, often from contact with cat feces or undercooked meat
- Bacterial infections from cat scratches or bites
-
Immune System Disorders:
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Indicators of Benign Lymph Nodes
Signs suggesting that swollen lymph nodes are benign include:
-
Localized Swelling: Nodes often enlarge near the site of infection, such as the neck, ears, or mouth.
-
Accompanying Symptoms: Symptoms like cough, body aches, or nausea may accompany the swelling, indicating an underlying infection.
-
Temporary Enlargement: Swollen nodes typically reduce in size as the infection resolves and the body recovers.
Common Locations for Benign Lymph Node Swelling
Benign lymph nodes can swell in various body regions, particularly where multiple blood vessels converge, including:
- Neck
- Armpits
- Chest
- Abdomen
- Groin
- Behind the ears
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
It is advisable to seek medical attention if lymph node swelling persists beyond two weeks or is accompanied by unusual symptoms such as fever or discharge. Healthcare providers can perform evaluations to determine the cause of the swelling and recommend appropriate treatment.
Diagnostic Approaches for Benign Lymph Nodes
To diagnose the nature of swollen lymph nodes, medical professionals may employ:
-
Clinical Examination: Assessing symptoms and medical history, and physically examining the nodes for size, texture, and tenderness.
-
Blood Tests: Identifying signs of infection or other underlying conditions.
-
Imaging Studies: Utilizing ultrasound, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to visualize the lymph nodes and surrounding tissues.
Management and Prevention
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause of the lymph node swelling. For infections, appropriate medications such as antibiotics or antivirals may be prescribed. Home care measures include rest, hydration, and warm compresses to alleviate discomfort.
Preventive strategies encompass:
- Maintaining good hygiene
- Adhering to a balanced diet
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Ensuring adequate rest
- Proper wound care to prevent infections
Understanding the nature of benign lymph nodes and monitoring for any changes are vital steps in maintaining health and well-being.
News in the same category


Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser
Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile
Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast
The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep
Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb

From White Hair to Black Hair Naturally in Just 5 Minutes — Fast Hair Growth Remedy

Boost Your Immune System Year-Round with Garlic, Onion, and Lemon
When You Start Eating 2 Eggs Every Day, Here’s What Happens to Your Body (Is It BAD??)
13 Warning Signs Your Kidneys Are Failing – Don’t Ignore These Symptoms

Save Your Heart: 8 Foods to Naturally Lower Cholesterol
Silent Signs of Artery Blockages Seniors Can’t Ignore
News Post
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN WE TONGUE KISS…See more

Nature’s Secret: 4 Healing Leaves That Support Metabolism, Immunity & Circulation Naturally

Don’t Drink Coconut Water Before You Know These 11 Secrets!

Pumpkin Seed Milk — The Natural Parasite Cleanser

Fast Rice Water Trick for a Brighter Smile

Morning Drink to Revive Your Kidneys Fast

The Onion Recipe That Could Transform Your Blood Sugar, Support Cleaner Arteries, and Protect Your Heart!

Top 4 Fruits That Help Your Kidneys Flush Out Toxins While You Sleep

Ginger, Clove, and Honey: The Natural Trio Your Body Will Thank You For

Heal 15 Years of Joint Pain Naturally with Turmeric and Honey Tea

This Juice Revived My Grandma’s Energy — Say Goodbye to Fatigue and Body Pain with This Natural Recipe

The Benefits of Eating 2 Boiled Eggs Every Morning: Transform Your Health!

If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Send You These 8 Signals — Don’t Ignore Them

The Surprising Effects of Avocado on Your Heart and Brain

Ways to Get Over a Man Who Didn’t Value You

I’m 66 but Look 36 — My Secret? Aloe Vera & Ginger for Firm, Smooth Skin

How to Make Okra Water to Treat 17 Health Problems Naturally

Banana and Egg Mask to Look Younger Even in Your 80s

Scent Leaf Secrets Unveiled: 10 Surprising Health Benefits of This Miracle Herb
