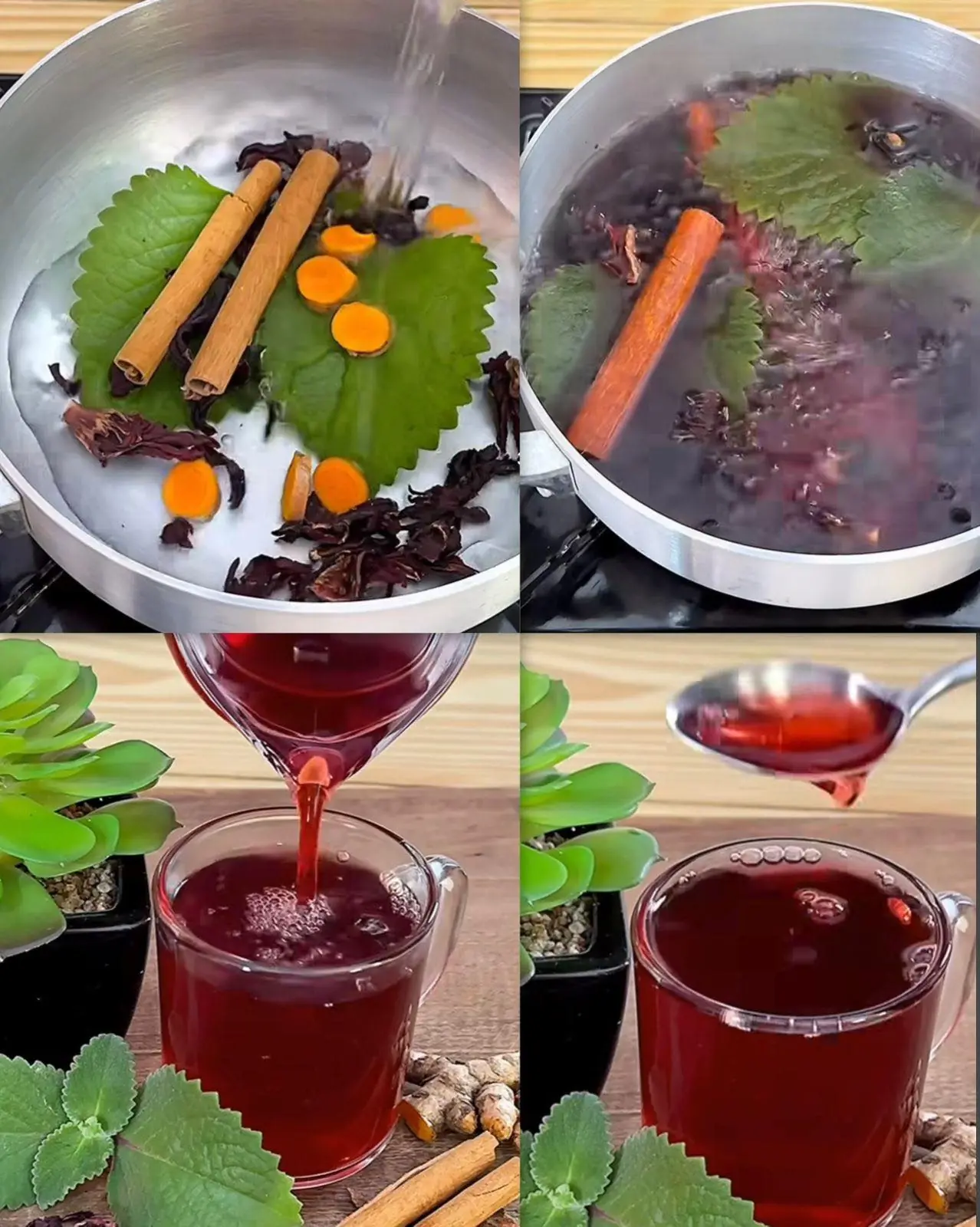

🌿 Natural Remedies for Inflamed Intestines
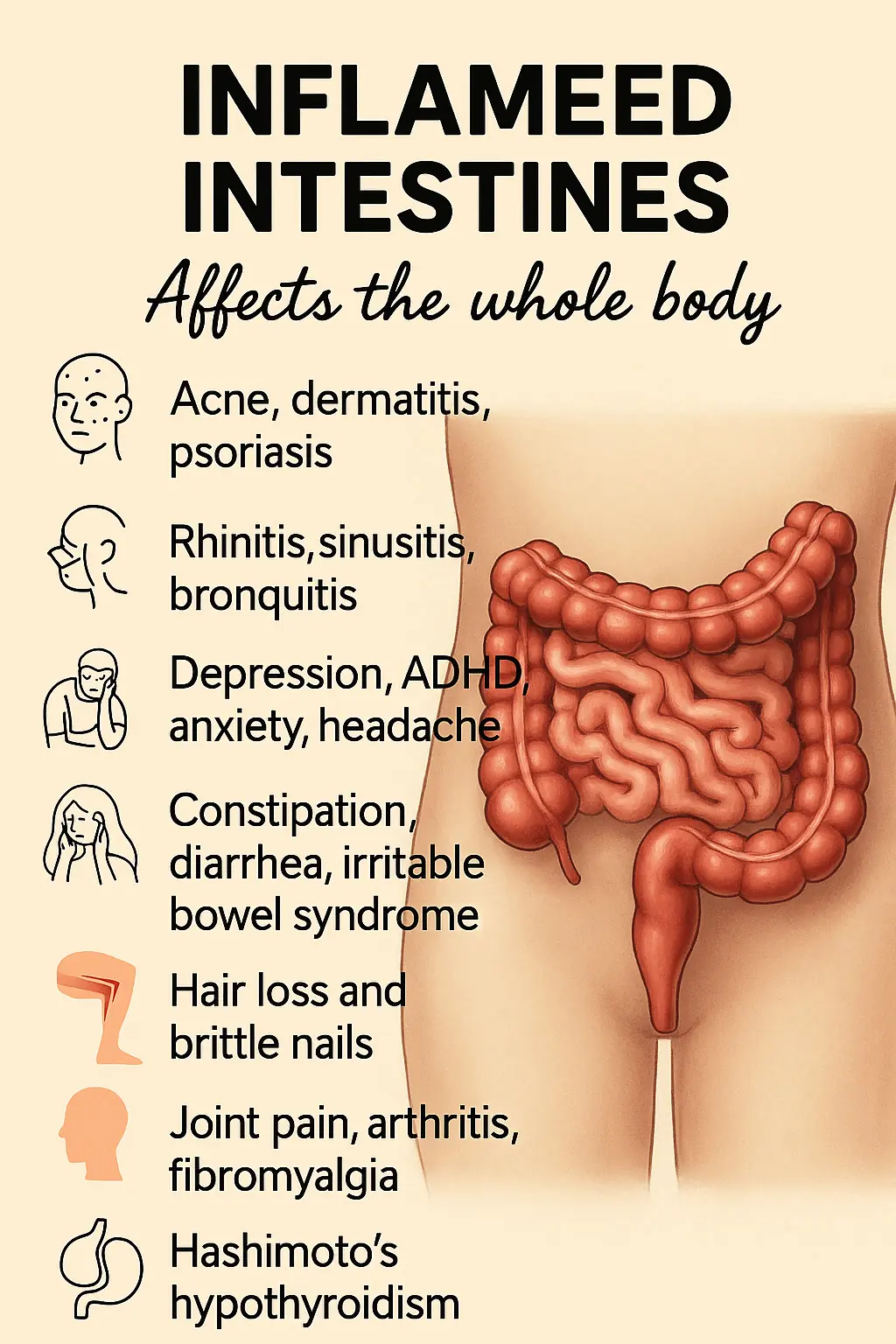
An inflamed intestine can result from conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, food intolerances (e.g., lactose or gluten), and intestinal infections. Chronic inflammation in the gut often leads to discomfort, bloating, pain, and irregular bowel movements. Incorporating natural remedies into your lifestyle may help manage symptoms and support healing.
1. Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla)
-
Active Compounds: Apigenin, bisabolol, flavonoids.
-
Benefits: Chamomile tea is widely used to calm the digestive tract. Its anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic properties help reduce cramping, gas, and bloating associated with IBS and colitis.
-
How to Use: Steep 1 tablespoon of dried chamomile flowers in hot water for 5–10 minutes. Drink 2–3 times daily, especially after meals.
-
Tip: Combine with fennel or peppermint for added digestive support.
2. Ginger (Zingiber officinale)
-
Active Compounds: Gingerols, shogaols.
-
Benefits: Ginger helps reduce gut inflammation and stimulates the digestive system. It also relieves nausea and abdominal pain.
-
How to Use: Boil fresh ginger slices in water for tea or take standardized capsules (250–500 mg up to 3 times daily).
-
Bonus: Ginger also promotes bile secretion, which aids fat digestion.
3. Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
-
Active Compound: Curcumin (powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory).
-
Benefits: Curcumin reduces inflammation in the gut lining, often used in IBD (Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis) management.
-
How to Use: Mix 1/2 tsp turmeric powder with black pepper in warm water, or take curcumin capsules (500–1000 mg daily with meals).
-
Important: Black pepper enhances curcumin absorption by up to 2000%.
4. Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis) – Pure Juice
-
Active Components: Polysaccharides, acemannan, vitamins.
-
Benefits: Aloe soothes and regenerates the intestinal lining, helping with conditions like gastritis, leaky gut, and IBS.
-
How to Use: Drink 1/4 to 1/2 cup of aloin-free aloe vera juice on an empty stomach in the morning.
-
Caution: Avoid if you have a sensitive stomach or experience diarrhea.
5. Probiotics
-
Types: Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Saccharomyces boulardii.
-
Benefits: Probiotics restore the balance of good bacteria in the gut, which is essential for reducing inflammation and strengthening the intestinal barrier.
-
How to Use:
-
Capsules: Look for high-quality products with at least 10 billion CFU.
-
Food Sources: Natural yogurt, kefir, kombucha, miso, tempeh, sauerkraut.
-
-
Best Time: Take on an empty stomach or as directed.
6. Flaxseeds and Chia Seeds
-
Nutrients: Rich in soluble fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, lignans.
-
Benefits: These seeds form a gel-like substance in the gut, which soothes irritation, promotes regular bowel movements, and reduces inflammation.
-
How to Use:
-
Soak 1 tablespoon of flaxseeds or chia seeds in water overnight.
-
Consume on an empty stomach or add to smoothies, oatmeal, or yogurt.
-
-
Hydration Tip: Drink plenty of water to avoid constipation.
7. Peppermint (Mentha piperita) or Spearmint (Mentha spicata)
-
Active Compound: Menthol.
-
Benefits: Relieves intestinal spasms, gas, and bloating. Peppermint oil has been clinically shown to improve symptoms of IBS.
-
How to Use:
-
Tea: Steep 1 teaspoon of dried leaves in hot water.
-
Capsules: Use enteric-coated peppermint oil capsules (0.2 mL), 1–2 times a day.
-
-
Note: May not be suitable for those with acid reflux or GERD.
8. Low-FODMAP Diet
-
FODMAPs: Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Mono-saccharides And Polyols.
-
Benefits: Reduces gas, bloating, and inflammation by eliminating poorly absorbed short-chain carbohydrates that ferment in the gut.
-
Foods to Avoid:
-
Garlic, onions, legumes, apples, pears, wheat, dairy with lactose.
-
-
Foods to Eat: Rice, oats, bananas, berries, zucchini, carrots, hard cheese, eggs.
-
Note: Best done under a dietitian’s guidance for long-term success.
🌱 Final Tips for Gut Health
-
Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to aid digestion and fiber movement.
-
Chew slowly: Proper chewing reduces digestive strain.
-
Avoid processed foods, alcohol, and excessive sugar.
-
Manage stress: Try yoga, meditation, or breathing techniques—chronic stress affects gut inflammation.
-
Sleep: Aim for 7–8 hours of restful sleep, as poor sleep disrupts gut balance.
News in the same category

Nature’s Pest Control with Garlic

Lemon Fat-Burning Drink – Melt Away Belly Fat!

Refresh Your Body with Lemon & Garlic Detox Remedy

Hair stylists won’t tell you this. 12 super hacks for thick, healthy hair

Mixing Cloves with Cinnamon for Powerful Health Benefits! 🌿🔥

Transform Your Skin with This Surprising Banana and Vaseline Mix!
Natural Intestinal Cleanse with Dates

Drinking Garlic Milk for Health Benefits

Natural Relief for Knee and Leg Pain: Banana, Red Onion, and Turmeric Remedy

Transforming Orange Peels and Ginger into a Health Boost for You!

Natural Ways to Remove Skin Moles at Home 🌿

Embrace the Okra Water Challenge for Better Health

Embrace Youthful Hair with Papaya Leaves!

A powerful, natural, and effective homemade keratin!

Garlic and Clove: Two Hidden Treasures for Your Health

ROSEMARY TEA ON AN EMPTY STOMACH

Spices and Lifestyle Tips to Clean Arteries and Prevent Heart Attacks👇

Say Goodbye to Diabetes, Fatty Liver, and Joint Pain with This Powerful Natural Remedy
News Post

Natural Herbal Remedy to Improve Circulation, Sleep, and Digestion

Nature’s Pest Control with Garlic

Lemon Fat-Burning Drink – Melt Away Belly Fat!

Refresh Your Body with Lemon & Garlic Detox Remedy

Hair stylists won’t tell you this. 12 super hacks for thick, healthy hair

Mixing Cloves with Cinnamon for Powerful Health Benefits! 🌿🔥

☕🍫 Espresso-Infused Mocha Perforated Cake

🍓🍫 Chocolate Raspberry Mousse Cake

Mary Berry Condensed Milk Ice Cream

🍫🎂 Epic Chocolate Overload Explosion Cake

☕ Classic Tiramisu Recipe 🍫

Signs That You Have Too Much Sugar in Your Blood

8 Foods You Should Be Eating to Help Kill Cancer Cells

8 Imperceptible Changes in Your Body that Could Be Warning of Health Problems

Decadent Chocolate Hazelnut Delight Cake Recipe

The Natural Snake Repellent That Sends Snakes Running — Safe for You, Deadly for Them 🐍❌

Volcano Eruption Triggers Tsunami Alert and Disrupts Flights in the Region

Transform Your Skin with This Surprising Banana and Vaseline Mix!
