Mouth Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Stages, and Treatment
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, is a type of head and neck cancer. It typically develops after the age of 40, and men are more commonly affected than women. In India alone, more than 77,000 new cases are reported each year, and over 52,000 deaths occur due to this disease.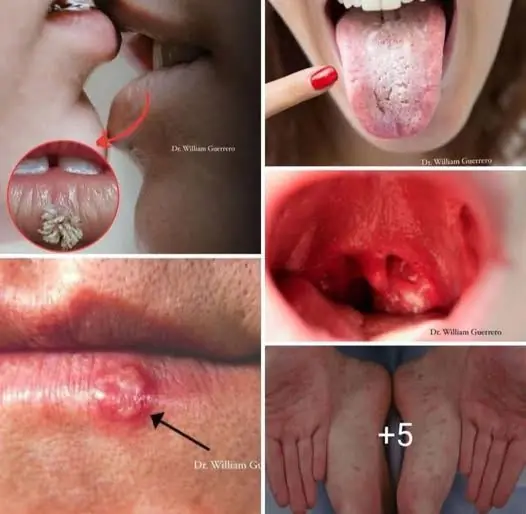
When detected early, oral cancer can often be treated successfully, but it is frequently diagnosed only after it has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck.
Types of Mouth Cancer
-
Lip cancer
-
Tongue cancer
-
Inner cheek cancer
-
Gum cancer
-
Cancer of the floor of the mouth
Dentists recommend having your mouth checked at least twice a year, especially if you smoke or drink alcohol regularly. Early detection significantly improves survival rates.
Common Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
In its early stages, oral cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, you should watch for the following warning signs:
-
Persistent sore or blister on the lips or inside the mouth that does not heal
-
Bleeding in the mouth
-
Loose teeth without clear cause
-
Pain while chewing or swallowing
-
Lumps in the neck
-
Earache
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Numbness in the lips, face, chin, or neck
-
Red or white patches on the tongue, lips, or mouth lining
-
Throat pain or dry mouth
-
Jaw stiffness or pain
-
Pain in the tongue
These symptoms do not always mean cancer, but they should never be ignored. If they persist, see a dentist or doctor promptly.
Main Causes of Mouth Cancer
-
Smoking – Cigarettes, cigars, and pipe smoking are the most common causes.
-
Tobacco in any form – Chewing or smokeless tobacco is also a major risk factor.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption – Drinking heavily increases the risk significantly.
Stages of Mouth Cancer
-
Stage 1: Tumor is less than 1 inch and has not spread to lymph nodes.
-
Stage 2: Tumor is 1–2 inches, but still not spread to lymph nodes.
-
Stage 3: Tumor is larger than 2 inches, or smaller but has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
-
Stage 4: Cancer spreads beyond the mouth to surrounding tissues, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body.
Knowing the stage helps doctors decide on the best treatment and predict recovery chances.
Treatment Options
-
Surgery – Removal of the tumor, sometimes followed by reconstructive surgery of the affected area.
-
Radiation therapy – External beam radiation or brachytherapy to target and kill cancer cells.
-
Chemotherapy – Drugs used to destroy cancer cells, often combined with radiation therapy.
-
Targeted drug therapy – Medications that attack cancer cells directly and prevent their growth.
Important Facts
-
Around 80% of cases are linked to tobacco use.
-
The average age of diagnosis is about 50.
-
Men are at a higher risk than women, and the risk increases with age.
-
Early detection gives an 82% survival rate, but in advanced stages, survival drops to around 27%.
Final Note
Maintaining good oral health and visiting the dentist regularly are the best ways to prevent oral cancer. If you notice unusual symptoms in your mouth, don’t delay—early treatment saves lives.
News in the same category

Research Suggests Your Body Knows When Death Is Near — And It Begins With the Nose
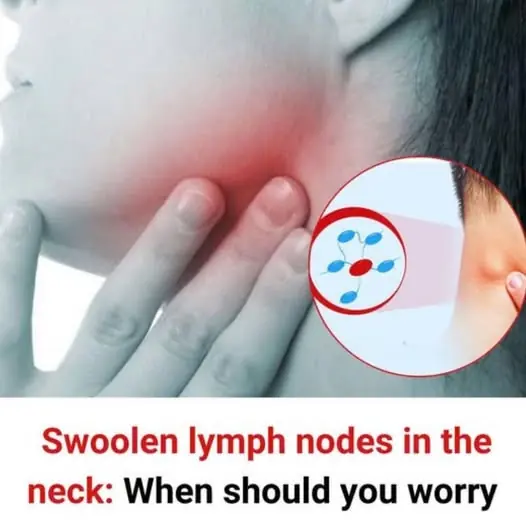
How to Identify Benign and Malignant Lymph Nodes
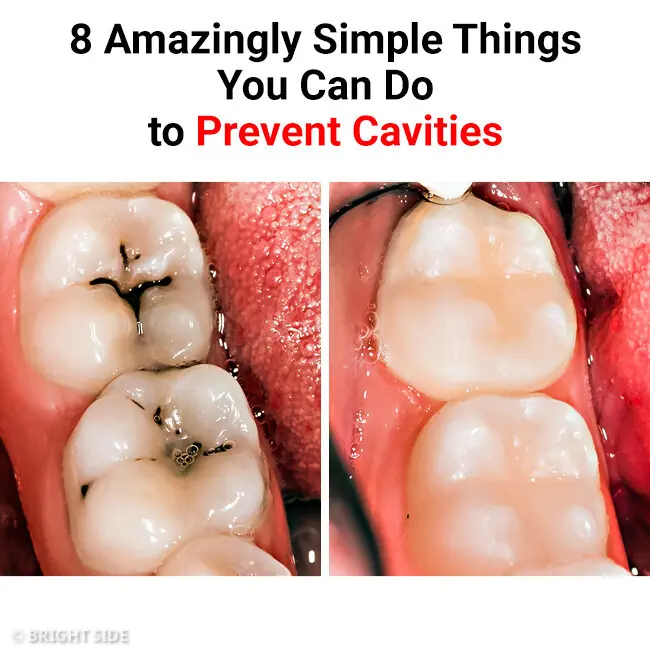
8 Surprisingly Easy Ways to Prevent Cavities
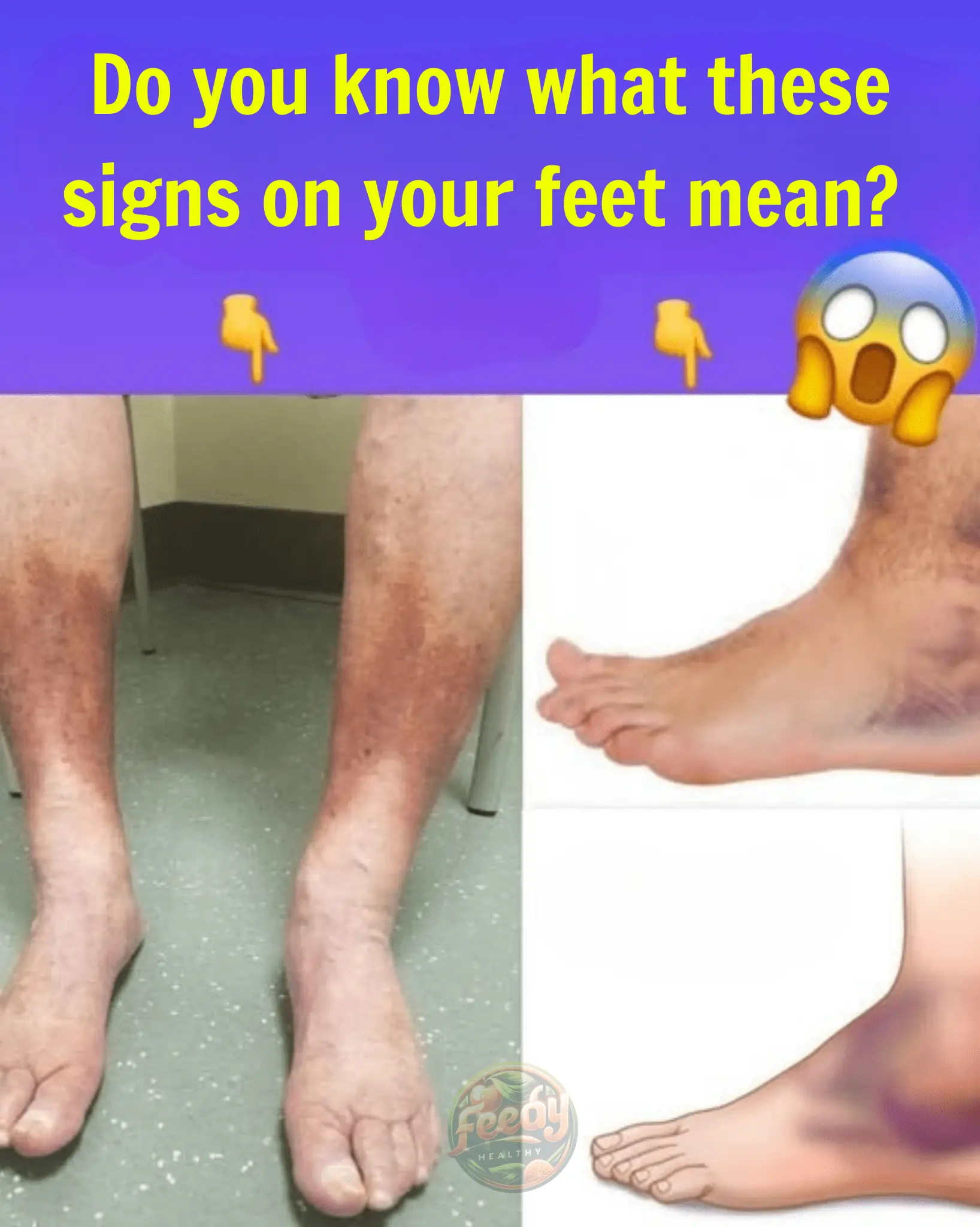
Do You Know What These Signs on Your Feet Mean?

2 Cloves a Day Trigger Irreversible Changes in Your Body — Especially After 40
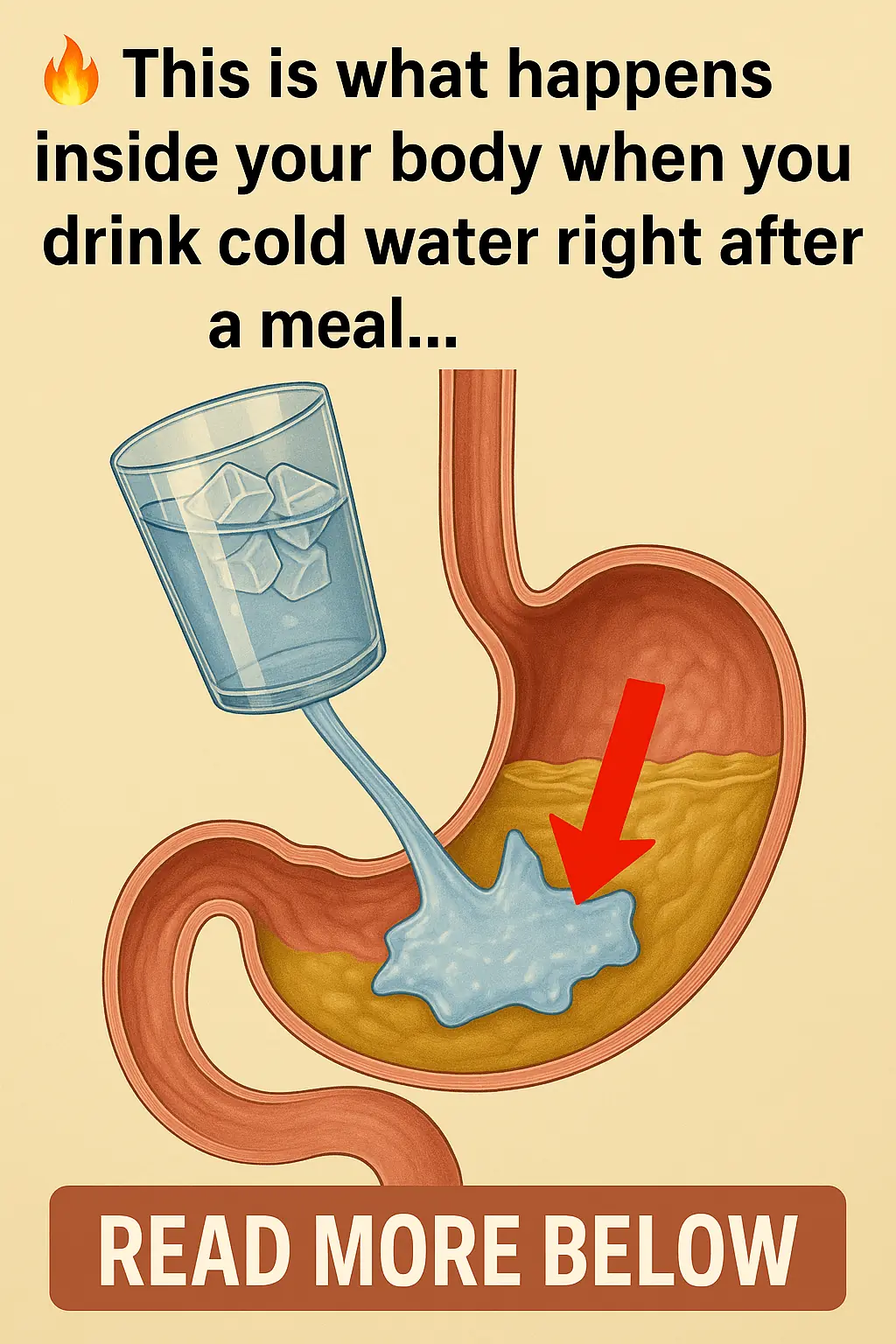
What Really Happens When You Drink Cold Water Right After a Meal?
A 5-Year-Old Girl Diagnosed With Late-Stage Cancer After Repeatedly Eating One Breakfast Food
6 Foot Symptoms That May Warn of a Heart Attack Weeks in Advance

Exercise: A Powerful Ally Against Cancer and Early Death

Breakthrough Cancer Vaccine Shows Remarkable Promise in Clinical Trials

The Power of Two Boiled Eggs: Health Benefits for Your Body

Why Gel Nail Polish Is Banned In Europe Starting Today – But Not In US
🍎 Apple Cider Vinegar Foot Soak: Benefits, Risks & What Science Says

Beets and Kidney Health: A Natural Tip for Later Years
11 Signs Your Body Is Giving You Important Alerts
A Boy’s Hand Shows Strange Signs After Playing in the Sand
What those strange skin patterns might really mean
What is Hand Dermatitis?
News Post

Mix Hibiscus Flower with Bay Leaves and Cinnamon

Homemade Onion Hair Oil for Stronger, Healthier Hair

Erika Kirk delivers emotional remarks after killing of husband Charlie Kirk
The Hidden Meaning of the “M” on Your Palm 🤲✨

10 Innocent-Looking Household Items That Can Cause Cancer (Backed by Science)

Eunice Foote: The Forgotten Scientist Who Predicted Climate Change in 1856

Research Suggests Your Body Knows When Death Is Near — And It Begins With the Nose

The drink that eliminates diabetes, fatty liver, poor circulation, and cancer without the need for expensive pills 👇

The drink that eliminates diabetes, fatty liver, poor circulation, and cancer without the need for expensive pills

Charlie Kirk shooting: Officials release video, plead for help in tracking down person of interest

California's Clean Air Vehicle Decal Program to End This Month

Family mourns 3-year-old boy hit and killed after running into street in Long Beach

Did Charlie Kirk start asking the wrong questions?

How to Identify Benign and Malignant Lymph Nodes

8 Surprisingly Easy Ways to Prevent Cavities

Take a spoonful of olive oil with lemon every day on an empty stomach.

Unlock the Secret to Glossy, Vibrant Hair with Cloves and One Simple Trick!

Nature’s Ultimate Detox Secret: Cucumber, Lemon, Celery, and Turmeric for a Healthier You!
Unlock Radiant Skin: The Colgate and Lemon Glow Secret You NEED to Know!