What happens when you cook with aluminum foil? Read this before cooking with it

What Happens When You Cook with Aluminum Foil? Read This Before Using It!
Aluminum foil is a kitchen staple prized for its convenience and versatility. From baking and grilling to food storage, it’s hard to imagine a modern kitchen without it. However, while aluminum foil is generally safe for short-term food storage, using it in cooking processes may carry potential health risks. This article explores how aluminum foil interacts with food, what happens when it is heated, and the possible health concerns associated with its use.
How Aluminum Foil Interacts with Food
Aluminum foil is composed of ultra-thin sheets of aluminum metal. Its lightweight and malleable properties make it ideal for wrapping food, but several factors can cause aluminum to leach into your meals, particularly when it’s used for cooking.
Factors That Affect Aluminum Leaching
-
Temperature:
High heat significantly increases the likelihood that aluminum will transfer into food. Cooking methods such as baking, grilling, and roasting expose foil to high temperatures, making leaching more pronounced. -
Acidic Foods:
Ingredients like tomatoes, vinegar, lemon juice, and other citrus products can dissolve aluminum more readily. When acidic foods come into contact with foil, more aluminum salts are produced and absorbed into the food. -
Salt and Spices:
The presence of salt, seasonings, or marinades can accelerate the reaction between food and aluminum foil, further increasing the rate of leaching. -
Cooking Time:
The longer food remains in contact with aluminum foil, the greater the opportunity for aluminum particles to seep into the food.
Key Takeaway: When cooking at high temperatures—especially with acidic, salty, or heavily seasoned ingredients—the risk of aluminum leaching into your food increases.
What Happens When You Heat Aluminum Foil?
Heating aluminum foil can cause it to break down at a microscopic level, resulting in tiny particles of aluminum transferring to your food. Here’s what happens under different cooking conditions:
A. Baking or Roasting in the Oven
-
Thermal Expansion:
When food is wrapped in aluminum foil and placed in the oven, the foil undergoes thermal expansion. As the temperature rises, the foil’s structure weakens slightly, allowing aluminum particles to break off and mix with the food. -
Duration Matters:
The longer the food is exposed to high oven temperatures, the more aluminum may leach out.
B. Grilling with Aluminum Foil
-
Direct Exposure to Flames:
Grilling exposes foil to direct flames or intense heat from the grill grates. This can cause the foil to degrade faster than in an oven. -
Flaking:
Under such conditions, small flakes of aluminum can detach from the foil and become embedded in the food, particularly when the foil is used to wrap or cover the food directly.
C. Wrapping Acidic or Salty Foods
-
Chemical Reactions:
When aluminum foil comes into contact with acidic or salty foods, it reacts to form aluminum salts. These salts dissolve in the food, leading to increased aluminum content. -
Enhanced Leaching:
The presence of acids or salts accelerates the breakdown of aluminum, making it more likely that these metal compounds will be ingested.
Key Takeaway: High heat, direct flame exposure, and the use of aluminum foil with acidic or salty ingredients can all contribute to a higher degree of aluminum leaching into your meals.
Health Concerns of Cooking with Aluminum Foil
While the human body can handle trace amounts of aluminum, concerns arise when it accumulates over time due to repeated exposure. Here are some potential health risks linked to cooking with aluminum foil:
A. Increased Aluminum Intake
- Cumulative Exposure:
Regular use of aluminum foil for cooking, especially under conditions that promote leaching, can lead to an increased intake of aluminum. Over time, this may result in the accumulation of aluminum in the body.
B. Neurological Concerns
- Possible Links to Neurodegeneration:
Some research suggests a potential link between high levels of aluminum exposure and neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. Although definitive evidence is lacking, long-term exposure remains a topic of concern among researchers.
C. Bone Health and Calcium Absorption
- Interference with Calcium:
Aluminum can interfere with the absorption of calcium, a critical mineral for maintaining bone health. This may contribute to bone density issues over prolonged periods.
D. Kidney Health Issues
- Processing Difficulties:
Individuals with kidney disease may have a reduced ability to process and excrete aluminum, leading to its accumulation in the body. This buildup can exacerbate existing kidney issues.
Key Takeaway: Although small, incidental exposure to aluminum is typically not harmful, frequent use of aluminum foil in high-heat or acidic cooking may increase long-term health risks, particularly concerning neurological health, bone density, and kidney function.
Conclusion
Aluminum foil offers undeniable convenience in the kitchen, but its use in cooking comes with potential risks. High temperatures, acidic foods, and prolonged contact can lead to the leaching of aluminum into your meals. While occasional use may be harmless, it’s important to be mindful of these factors, especially for individuals with preexisting health conditions.
For those looking for safer alternatives, consider using parchment paper, silicone baking mats, or glass and ceramic cookware when cooking at high temperatures or with acidic ingredients.
Before you wrap your next dish in foil, take a moment to weigh the benefits against the potential risks. By making informed choices in your kitchen, you can protect your health while still enjoying the convenience that modern cooking tools offer.
Stay informed, cook smart, and keep your meals as safe as they are delicious!
News in the same category

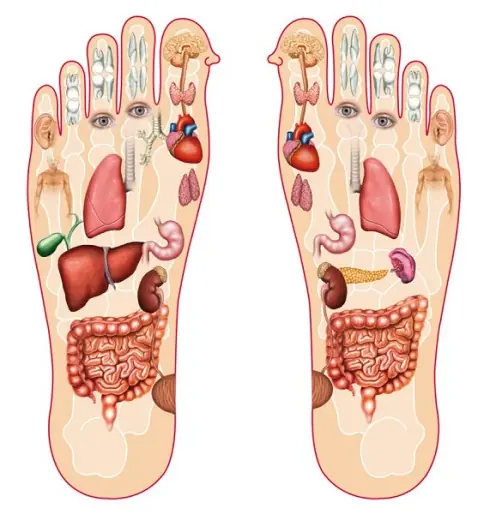
LISTEN TO YOUR BODY! Discover 10 subtle nutrient red flags and the easy fixes that can transform your health!

The Surprising Impact of Sleeping Pills on the Brain’s Cleaning System 🧠🛏️

What happens when you cook with aluminum foil? Read this before cooking with it

Revitalize Your Health: The Ultimate Beetroot & Lemon Detox Elixir for Colon Health and Weight Loss

Sumac Tree Benefits – A Powerful Medicinal and Culinary Plant

Mulberry Magic: Unleashing the Health and Flavor of Homemade Black Mulberry Jam

Okra Unleashed: Unlocking the Nutritional Power and Culinary Magic of Lady's Finger

Basil Flower: The Fragrant Elegance of Aromatic Blossoms

Drink This Once a Day and Transform Your Health!

Taro Root (Colocasia esculenta): Uses, Benefits, and Healthy Recipes

Creamy Garlic Parmesan Tortellini with Sausage and Broccoli

Next-Level Teriyaki Chicken Power Bowl 🥦🍚🥒

Watermelon, Carrot, Beetroot, and Ginger Juice: A Refreshing Drink with Incredible Health Benefits
Experts who predicted covid say new virus appearing in US could threaten 'all of mankind'

SCIENTISTS FIND BEETHOVEN'S 5TH SYMPHONY DESTROYS 20% OF CANCER CELLS VS WHEN NO MUSIC IS PLAYED, AND IT LEAVES HEALTHY CELLS

10 Benefits of Pigweed (Amaranth)

Carob: Health Benefits, Culinary Uses, and Sustainable Recipes

Natural Healing Tonic: A Powerful Herbal Drink for Diabetes, High Blood Pressure, and Circulation
News Post

With this shampoo, you’ll put an end to hair loss and even stimulate hair growth on your forehead.

Goosegrass: A Hidden Natural Remedy with Remarkable Benefits

Chayote Juice: A Natural Remedy with 13 Remarkable Health Benefits

LISTEN TO YOUR BODY! Discover 10 subtle nutrient red flags and the easy fixes that can transform your health!

The Surprising Impact of Sleeping Pills on the Brain’s Cleaning System 🧠🛏️

Forget Tomato Seeds: Just Plant a Few Slices from the Store. Here’s How

Revitalize Your Health: The Ultimate Beetroot & Lemon Detox Elixir for Colon Health and Weight Loss

Sumac Tree Benefits – A Powerful Medicinal and Culinary Plant

Golden Crispy on the Outside, Soft & Fluffy Inside: A Perfect Pan-Fried Breakfast Bread

Mulberry Magic: Unleashing the Health and Flavor of Homemade Black Mulberry Jam

Okra Unleashed: Unlocking the Nutritional Power and Culinary Magic of Lady's Finger

Basil Flower: The Fragrant Elegance of Aromatic Blossoms

How to grow Cinnamon trees

Bedbugs: Effective Ways to Eliminate Them from Your Home

Regularly Eating Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast: 3 Visible Health Benefits You Shouldn't Miss
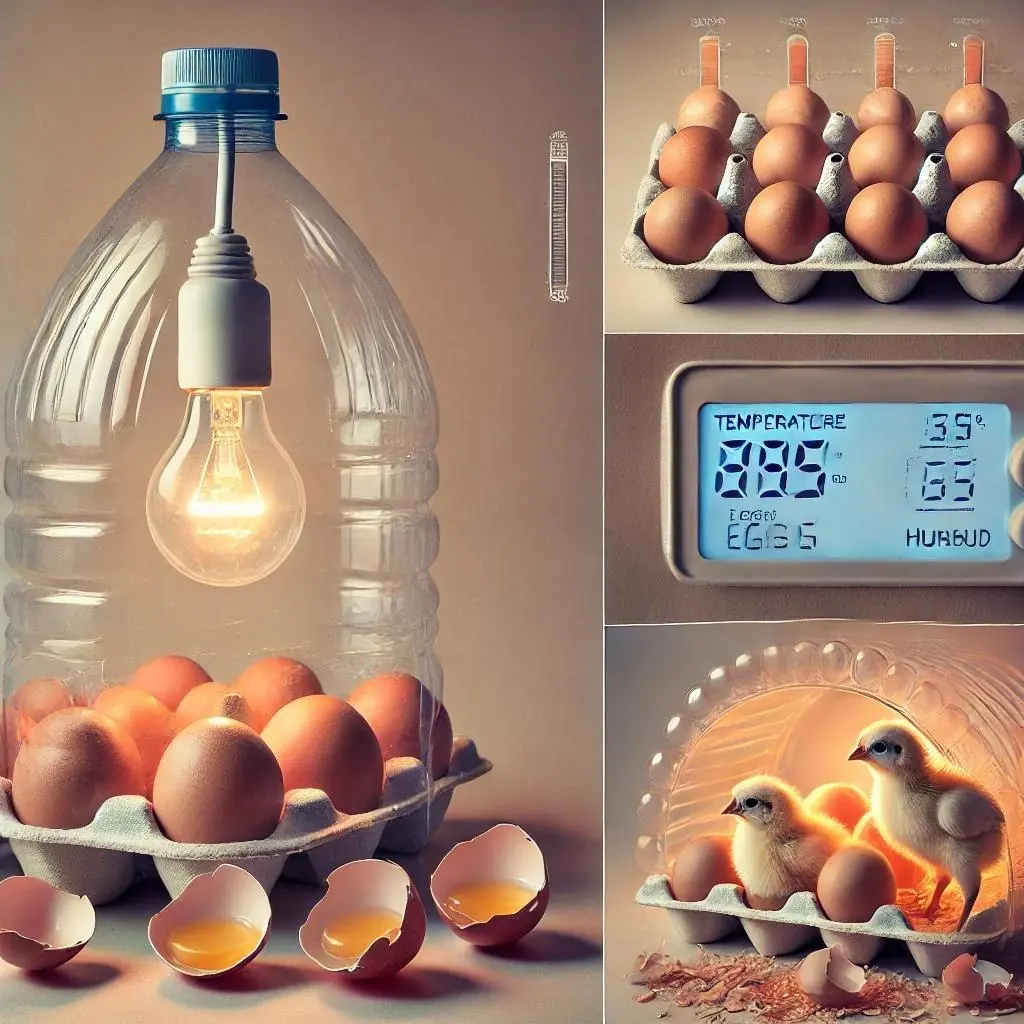
How to Build a Homemade Egg Incubator Using a Water Bottle

Banana Avocado Pistachio Smoothie

Drink This Once a Day and Transform Your Health!